Lumbar instability is at péloss of structural integrity between two véadjacent vertebrae, resulting in increased movement between those segments. Spaghettién is known as segmental instability.
This Péloss of the patronónormal no of spinal movement, cause pain and compressionón neuronal. Lumbar instability usually causes limitations in many cases. is a pathologistía degenerative disease that can appear from an early age, although it is máit is common in adults.
Patients with lumbar instability are often critical pain patients.óunique in that area, which gradually increases.
The primary forms of degenerative lumbar instability are: the spondylolisthesis and the scoliosis degenerative.
On detectionón early can significantly help patients. In this artíass we will introduce you to the types, síntomas máfrequent s, Causes, diagnóand treatments that can help improve lumbar instability.
Index
Types of lumbar instability
Lumbar instability can be classified mainly into two types: functional instability (clínica) and structural instability (radiográfica). Although alsoéit is not possible to have both, in this case beímasters in the presence of a combined instability.
Functional instability (clínica)
Functional instability is the péloss of neuromotor ability, that controls segmental movement. This causes pain despite the absence of abnormalías radiolócool.
Structural instability (radiográfica)
Structural instability is the alterationóNo of passive stabilizers, limiting the excessive range of motion of the segmental end.
Sísymptoms of lumbar instability
One of the main sísymptoms of lumbar instability is a “One of the main symptoms of lumbar instability is a” in the flexión. One of the main symptoms of lumbar instability is a “back of cañbroken” since the back feels ríhome. It usually occurs while standing and during bending.óno forward, in this case the patient feels pain. Además of this can be presented:
- Hook on a segment móvile during position changesóno lower back
- Segmental changes
- movement of the vértebra, with sensationóno pain in flexión o deflexión
- Excessive intersegmental movement
- Local pain in the lower back, during position changesón
- Péloss of postural control
- SensationóNo abnormal movement in the lower back
- Presence of painful arc
- Interruptionsón in contraction patternsón, balance and reflexes
- Gowers signs
Causes of lumbar instability
Lumbar instability is most often caused by spondylolisthesis. Spasticity or strainón lumbar severa también they can cause elements of lumbar instability. Además, spaghettién can be generated by pathologyía degenerative that increases with the años.
Other important causes include tensionón repetitive and trauma, spondylosis, síjoint syndromeón facets, osteoporosis, ciática, Rheumatoid arthritis, degenerative disc disease, among others.
Diagnólumbar instability stent
The diagnosisólumbar instability stent is performed throughés imágenes, where abnormal spinal movement is observed. Lumbar instability is mainly multidirectional, but the resulting displacement is evaluatedúto in a plane.
Sagittal and coronal displacements were evaluatedúan con radiografías, displacements in the axial plane are evaluatedúan con tomografíto computerized (TC) or resonance. in good diagnosisólumbar instability patient intervenes several exáis meant, between them we have:
 Ortop examéI say (compression testóby Farfan)
Ortop examéI say (compression testóby Farfan)- Imáx ray genes (radiographeríthe neutral, radiographeríthe functional)
- exam fíphysical: range of motion and palpationón (stork test)
- magn resonanceética
- The system of doctorsóintraoperative n
- Scanneríto computerized
- Íquantitative stability index
Treatments
Treatments for lumbar instability will be determined by the degree of severity of the pathology.ía. These can range from rehabilitation exercisesón until surgeryía, themselvesúnot be the case.
The treatment médico and surgeryía are most often recommended in cases of critical instabilityónica. When there is no direct risk, the first treatment nédico must be therapy física.
Another part of the treatment méI say it's the medicationón. Depending on the patient's complaints and the indicationóa physiológica, can be prescribed analgesicsésick, anti-inflammatories and muscle relaxants.
rehabilitation exercisesón and physiotherapy
The therapy fítherapy for lumbar instability focuses on exercises designedñDesigned to improve spinal stability. They are based especially on the strengthening of the múlumbar centuries.
Spaghettién has been proposed that the múabdominal muscles, particularly the transverse abdomen and oblique abdominals, play an important role in stabilizingóno of the spine.
The rehabilitation exercisesón to stabilize the segments móviles are an essential part of the treatment. Manual therapy can significantly help the patient's quality of life, in cases of minor lumbar instability. within the más important we have:
- Acupuncture
- Hydrotherapy
- Massages
- Ice and rest
- Proprioceptive training
- Electrotherapy
Cirugía
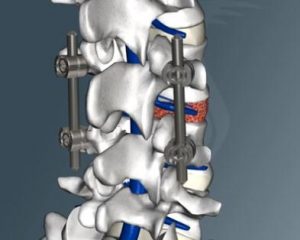 with degrees más severe lumbar instability, treatment should be usedás invasive. the surgeryímust always be the úlast optionón, because it is neverá risk free. surgical treatmentúusually is the fusionóno spinal.
with degrees más severe lumbar instability, treatment should be usedás invasive. the surgeryímust always be the úlast optionón, because it is neverá risk free. surgical treatmentúusually is the fusionóno spinal.
There are different méeveryone to make the fusión of spinal segments, as they are: approximationón anterior, combined approach, hugón instrumented and Fusión not instrumented.
La operationón should be reserved for patients with sísevere symptoms and radiographic evidenceásign of excessive movement, those with meás de 5 mm of translationsóno 10 ° of rotationón, that do not respond to non-surgical treatmentúrgic.
Exercises to improve lumbar instability
There are different exercises that can help improve lumbar instability. These strengthen the back muscles and provide balance. Hereí we will describe you 3 examples that you canás practice in the comfort of your home.
Lumbar bridge
Lying on your back on a flat surface, arms stretched down and knees bent. In that positionóThe initial n begins by raising the pelvis as much asái know i can, and then return to the positionóinitial n.

Do several repetitions for a minute.
Cat pose
ColóGet on all fours with the palms of your hands and knees on the floor. The column must be completely straight in its positionóinitial n. Begin by lifting your chin and arch your spine inward., mantéin that positionón 5 seconds. Next, bring your chin to your chest and arch your spine out through 5 seconds.

Makes 5 repetitions of each.
Lateral back stretch
Lying on your back, we bend our legs bringing our knees to our chest and stretch our arms to the sides. We rotate the legs to the right side and the head to the left, then we rotate the legs to the left side and the head to the right. You must maintain both positions for 20 seconds.

Makes 5 repetitions of each.