Back pain is a common complaint.ún, but when it happens suddenly and alsoén includes sudden numbness in the área genital, Difficulty urinating, and leg weakness – it is an emergencyétip.
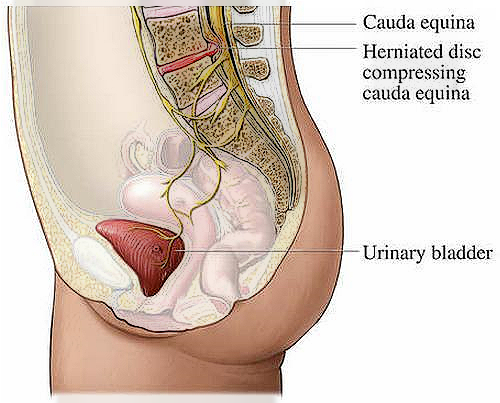
He sícauda equina syndrome or cauda equina is often caused by a large herniated disc in the regionón lumbar, that compresses the raínervous breakdown at the end of the méspinal game
These nerves envían messages to and from the bladder, intestines and legs. If they keep squeezed too long, it can happen one dayño irreversible.
the surgeryíimmediately to relieve pressureócan't prevent one dayñor permanently and restore bladder and functionón intestinal.
Index
¿Whaté is the sícauda equina syndrome or cauda equina?
He síCauda equina syndrome is a rare disease, but it has serious consequences if left untreatedápiously.
It is most often due to a large herniated disc in the regionón lumbar, that compresses the raínervous breaks at the end of the méspinal game.
It's coolínerve cells are grouped together and resemble a horse's tail. This is how it gets its name. Equine tail means “horse tail” in the Tín.
Unlike the oldería of back problems that are long-standing or criticalónica, ponytail is an acute event, like a stroke or heart attackón. It most often develops rápiously, within so sóit 6 a 10 hours.
The síntomas clásick are back pain, along with the appearanceóNo sudden numbness in the ágenital area and retentionón sudden urinary, are signs of an emergencyétip.
Aliviar including itón way ráask can determine if the patient resumes a normal life or lives with incontinence and parálysis of the legs.
Less frequently, in people with recurrent back problems, ponytail may appear gradually, with a progressionón slow of the síurinary symptoms.
Because he síCauda equina syndrome is a disorder of the nerves that control the bladder., the sísymptoms may be similar to those caused due to problems with the bladder or próstata.
Sícauda equina syndromeíntomas
The síntomas de la inclusiveón of horsetail include problems with the bladder, the intestine or the functionón sexual, Difficulty urinating (retentionón) or trouble containing them (incontinence).
The biggestíof people have sharp pain in the lower back and glúteos, así such as numbness and tingling in the “saddle area” (rectal and genital areas and inner thighs).
Pain can travel down the back of the thigh, más allá knee, calf and foot (ciática). An individual may experience weakness or parálysis in the leg or foot, especially when getting up from a chair.
Weakness in the legs and péextreme loss of bladder or functionóIntestinal n are signs of an emergency; if this has happened, seek help mésay right away.
¿Cuáthey are the causes?
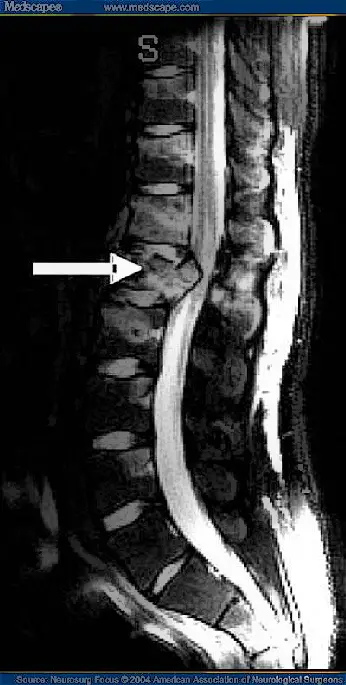
A herniated disc can cause the sícauda equina syndrome. During a hernia, the gelatinous center of a spinal disc can bulge or rupture throughés of a áevil débil in the disc wall and compress the nerves.
in the majoría of the cases, herniated disc occurs at the L4-5 or L5-S1 discs in the lumbar spine. An injuryón sports, a caíday or a car accident can fracture the spine or tear a músculo and dayñar the nerves.
Other causes include narrowing of the spinal canal. (stenosis), a tumor, an infectionóno hemorrhage.
¿Cóhow the diagnosis is madeóstico?
A review mécareful physician can confirm or rule out a diagnosisósuspicion of cauda equina. The evaluationón includes a history clínica and exam fíphysical. One péloss of sensation in the anal area is a conclusionón clara.
A patient complaining of severe leg weakness, numbness in the área genital, o péloss of functionóNo bladder or bowel will undergoá to a magnetic resonanceétics to reveal the degree to which the hernia isá compressing spinal nerves.
The méI say tambiéCan't order a CT scaníCT or myelographyía.
Cauda equina syndrome surgical treatment
For a patient with síacute cauda equina syndrome, the surgeryíto probably an urgent need.
The goal is to relieve pressureón on the spinal nerves to restore functionómuscle n and sensationóno bladder, intestines and legs.
Depending on the cause, one of the following surgeriesíthis is how it can be done:
Discectomía
For one herniated disc eliminate in pigsónumber of the disk that isá compressing the nerves. The surgeon makes a smallña pearlón in the center of the back.
The Múoscules of the spine move to the side to expose the vértebra ósea.
A window of the bone is removed to expose the raíz of nerve and disc. To pigsón of the ruptured disc compressing the spinal nerves is carefully removed.
decompressionón spinal for stenosis:
removes dewclaws óbones and ligaments that compress the nerves. a little oneña pearlón in the back.
The surgeon removes the bone that forms the roof of the spinal canal. thenón, soft tissue and bone are removed to create más room for nerves.
Tumors and other lesions alsoécan't be removed.
Trials clíunique
Trials clíthey are only research studiesón in which new treatments – drugs, diagnóstatic, procedures and other therapies are tested in people to see if they are safe and effective.
The investigationón is always carried out to improve the stateáattention spanón métip. La informationón on cl trialsícurrent unique, including eligibility, protocol and places, are on the web.
Studies may be sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, así such as private industry and companiesñíthe pharmaceuticalséuticas.
Sequelae and postoperative cauda equina syndrome
Some functions of the bladder and bowel are automatic.áticos, but those under voluntary control can be lost if you have the sícauda equina syndrome.
This means that you may not know when you need to urinate or have a bowel movement., or you may have a hard time doing it.
The recoveryón of sícauda equina syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms.ísymptoms and durationón of the compressed nerves before the surgeryíto be done. The possibility of recoveryófull n for those who have withholdingón urinary is minor [1,2]:
Of those who have experienced numbness and tingling in the genital area (CES incompleta), the 90% recoveredó normal bladder, the intestine and the functionón sexual.
Of the people who suffer from withholdingóno bladder (CES completa), the 20% may have permanent incontinence and péloss of sensation in the ábad pélvica.
residual problems afterés of the surgeryía may take a few months to resolve. They may be necessary métodos de rehabilitationón, like bladder retraining.
People who suffer permanent injuries faceán challenges in their daily lives. Physical Therapists Can Help You Learn Important Self-Care Skills, including self-catheterizationón, stress managementés y térelaxation techniquesón.
Additional assistance can be provided by a social worker, a support group, a sex therapist or psychiatrist (for depressionón).
On rare occasions, torque can be producedálysis of the legs.
