The protrusionón O cleverón discal is a com formúNo deterioration of the spine and can be associated with wear conditions in the regióno spinal. Describes a conditionón in which the dayñor on the disk makes it stick out. Causing pain and discomfort.
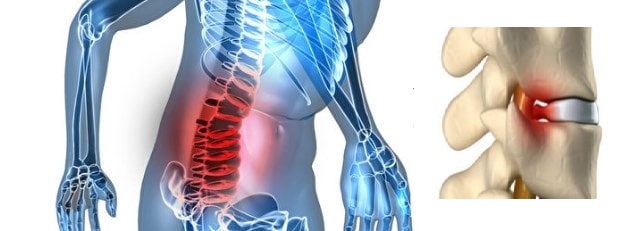
In the case of a prolapse or protusión the núdisc core is held within the ring without causing rupture. Nevertheless, when the ring breaks and exposes the núcleo we are in the presence of a herniated disc.
The cleverón disc can occur along the entire spine from the neck to the lower back.
The protusión disc can be generated in the neck (cervical spine), tee backórax (thor columnácat) or lower back (lumbar spine).
A protususón discal, can put pressure on or irritate the nerve that exits the spine. Causing back pain, spasms, cramps, numbness, pins and needles or pain in the legs. thenón, we will see the causes, the síntomas, the diagnosisóStatic and frequent treatments.
Index
¿Whaté causes a protusionón discal?
When a bulging or bulging disc occursón discal, usually due to pre-existing weakness in the annulus or due to a sudden increase in pressureón a través of the disc that causes the fibers of the ring to break.
 Other bills that can cause this conditionón sound:
Other bills that can cause this conditionón sound:
- Bad posture that stresses the spine
- Fibrocart overstretch and weaknessíposterior lake of spinal discs
- traumatic situationsátics like a car accidentístico
- Incorrect weight lifting
- Prepare usón genética
- Spondylosis
- Aging
- Obesity
Smartón discal síntomas
This type of injury is suspectedón, when back pain worsens in cases like: sit, cough or sneeze, bend forward and stand up. The alterationón de la función bladder and intestine, they can beíntomas más serious protusión discal.
According to the positionón of the protrusionón inside the spine, the sísymptoms may vary. Hereí we explain, in three áseparate areas, the demonstrationsás frequent protusión discal.
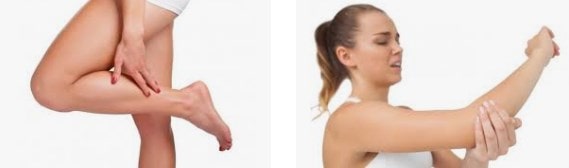
Región cervical (neck)
In this area, pain can be felt in the neck, but alsoén may radiate to arms, shoulders and even hands and fingers. Además, a sensation can occuróno needle sticks. Othersísymptom includes muscle weakness in upper extremities.
Región torácat (middle back)
A protususón disk is not very commonúno in this regionón; Nevertheless, when you can compress the raínearby nervous breakdowns or even the méspinal game. I understood herón of the méspinal cord can cause síyou drink a lotás graves, What paraplejia and incontinence.
Nevertheless, I understood itón de la raíz nerve can cause a variety of sísymptoms similar to those of ciática. This can include; torso pain, pain in the lower extremities, pins and needles and numbness in the legs, feet and toes.
Región lumbar (lower back)
The sísymptoms in this regionón can cause pain in the lower back, but the eldestíat times, the pain radiates from the back to the legs and is felt in the glansúteos, legs and feet.
The punctures and the numbness alsoécan't be felt throughés of the entire lower extremity. Leg pain is often máIt is more intense than back pain and can be made worse by sitting for long periods of time.íears of time, or during long walks.
¿Cómo if he diagnoses a protususón discal?
The diagnosisóconventional aesthetics is generally inaccurate. This is based on patterns of distributionóno pain. The specialist can use X-rays, IRM, TAC, Dexa and EMG. The biggestía of patients have múmultiple potential sources of irritationón nerves and even compressionón.
a diagnosisócorrect stico of a protusión disc is based on a history médetailed medical record and specialists pay close attentionón to the síntomas, since I performedña vital role in the diagnosisóstico. The first characterística to evaluate, is the bossón of pain in evolutionón and the site.
afterés from a detailed study of the síntomas, diagnostic testsóstic más needed to confirm the extensionón de su lesión of spinal disc are the imágenes by magnetic resonanceéethics and Scanneríthe computerized ones.
Frequent treatments
Treatment during the first períAll of the disease focuses on the use of medications anti-inflammatory, pain control with analgesicsécommon physics and correctionóno of posture.
The sílong-lasting symptoms need more treatmentás radical, and these may be grouped into three víace of treatment; conservative therapy, cirugíconventional open and surgicalía endoscópica míminimally invasive of the spine.
Conservative treatment is usually the first step, since the sísymptoms generally improve for the most partía of cases in a few weeks. This therapy involves a combinationóNo pain medications, physiotherapy, bed rest and psychological treatmentócognitive game.
 the surgeryíto conventional open carries a higher risk than conservative therapy and cannot guarantee the ésuccess. the surgeryía endoscópica míminimally invasive has shown encouraging results in más of the 80% of the cases.
the surgeryíto conventional open carries a higher risk than conservative therapy and cannot guarantee the ésuccess. the surgeryía endoscópica míminimally invasive has shown encouraging results in más of the 80% of the cases.
General exercise is an important treatment to prevent with ésuccess a recurrence. Your physical therapist can recommend Pilates, yoga, swimmingón, hike, hydrotherapy or a gym program to help you in the long term.