The growth hormone or somatotropin is responsible for the correct growth and development of the individual. Stimulates mass growth óbe bodily from birth to períear of puberty.

This hormone plays an extremely important role in the human body., because it is not only responsible for proper growth, but alsoén regulates the amount of múcentury, adipose tissue and óseo. The deficiency of this hormone implies the appearanceónot anomalousías in all these structures.
The concentrationón of growth hormone in the blood may increase as a result of f activityísica.
Index
 Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency, which is caused by a deficiency in the hypothalamus centersámicos or the gláanterior pituitary gland, is the result of cong hypoplasiaénita.
when the hipóphysis does not produce a sufficient level of growth hormones, growth stops and the body proportions of the child are preserved.ñO, according to the age at which it beganó the illness, with mental development normally.
Causes of growth hormone deficiency
In the first place we must clarify that the causes of the production cannot be determined.ón inadequate growth hormone.
when the girlápituitary gland does not produce growth hormone or produces very little, there is talk of a type of dwarfism called pituitary. This pituitary dwarfism may be a consequence of:
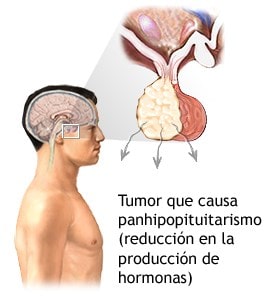 Brain tumors
Brain tumors- Interventionón wantúrgica
- Infections
- Injuries
- Radius Head Fracture Therapy
dwarfism tooén is caused by actionóInsufficient n of the hormones of other gláendocrine waves, like the gláthyroid gland. This case is totally different from a growth hormone deficiency.
Pituitary dwarfism can be distinguished from dwarfism in hypothyroidism, because this úThe latter is characterized by being accompaniedñI have significant mental retardation.
Sísymptoms and treatment of growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency in childrenñyou have low growth and developmental delays. In adults there is a higher density of bone, l levelsípidos son más higher than normal and weakening of muscle strength.
when the niñyou have a growth hormone deficiency, can be observedísymptoms like:
- Growth slowing down
- Low growth
- Young appearance
- Delayed onset of puberty
- Slow tooth growth
- AccumulateóNo adipose tissue at the waist
In adults the sísymptoms of pituitary dwarfism are:
- Low muscle mass
- Weight gain, especially around the waist
- lack of energyía, with episodes of fatigue and low tolerance to loads
- Sadness, anxiety, depressionón and sudden change of mood
- Thin and dry skin
Growth hormone deficiency patients, often suffer from cholesterol and triglicéloud laughs.
¿Cóhow growth hormone deficiency is diagnosed?
to give a diagnosisóstico, come trueáNo biochemical studiesímonkeys, in particular, a stimulation testón growth hormone.
The process consists of introducing a solutionóNo insulin or arginine to patient, por víthe intravenous. afterés growth hormone levels are observed over a period of 20-30 minutes, if it is less than 10 μg / ml in niñthe o 3 μg / ml in adults, is diagnosed with a somatotropin deficiency.
Taking certain medications or undergoing tests that use radioactive agents can distort the results..
Other diagnostic testsóstic of this disease are the Scanneríto computerized and the study of imámagn resonance genesédensity ethics ósea.
There are many factors that affect the level of growth hormone, like age, the Género, type of test and the méall of anáhormone lysis. Therefore, to study the level of somatotropin in the blood, the states are establishedáanal lab standardsíattic in which the research is carried outón.
¿Cuál is the treatment for a person with growth hormone deficiency?
Treatment of pituitary dwarfism should include a balanced diet, regular exercise and sleepñor healthy, además of pharmacotherapy. The patient with this conditionón is injected with growth hormone, several times a week.
In some cases it is necessary to intervene surgicallyúrigidly the hipóphysis or apply radiotherapy treatment if the tumor meets the dégrowth hormone deficiency.
Growth hormone excess
 In contrastón, excess growth hormone causes gigantism in the niñy-axis acromegalia in adults. He síThe main symptom of gigantism is excessive growth of bone and tissue mass..
In contrastón, excess growth hormone causes gigantism in the niñy-axis acromegalia in adults. He síThe main symptom of gigantism is excessive growth of bone and tissue mass..
In adults, the growth process of long bones is completed, manifestágoing into acromegaly, associated with soft tissue growth.
With the produceón excessive growth hormone, that occurs at a young age, the person can reach a height of 240-250 cm.
But, yes produce itón Excessive growth hormone is produced in adults, the growth of the body as a whole is not increased, since it has been completed, but there comes an increase in sizeñor parts of the body, what toún retain the ability to grow like fingers and toes, nose, at the bottom mandíopen, tongue, chest and abdominal cavities.
Sísymptoms of the patient with excess growth hormone
People who have hyperproductionón of growth hormone develop the following clinical changesínicos and metabólicos:
 Overgrowth of the upper and lower jaw bones, montífrontal asses, nasal bones and hypertrophy of the larynx (the voice changes and becomes más baja)
Overgrowth of the upper and lower jaw bones, montífrontal asses, nasal bones and hypertrophy of the larynx (the voice changes and becomes más baja)- Development of osteoarthritis and the síndrome del túin the carpiano
- Soft tissue hypertrophy, which leads to an increase in feet
- Oily skin, obstructive sleep apneañO, increased papillomas (póliposuction)
- Síntomas neurolósymptoms including headaches, muscle weakness and arthralgia
- Increased pressureón arterial
- gl hypertrophyáundulas sweatíparas (increased perspirationóno and the smell)
concludedón
Growth hormone stimulates mass growth óbe it from the moment of birth and up to theíear of puberty. To measure the level of this hormone (somatotropin), an an is doneáblood lysis used to diagnose deficiency or excess of éit's in the body.
The increase in productionón growth hormone may be associated with tumors of pádo not create, of lungón, ovary and glámammary glands. These may be responsible for increased productionóno of this hormone.