while the teaéterm “stenosis” comes from Greek and means “suffocation”; spinal stenosis, Nevertheless, has little in comúwith suffocation.
There are two types of spinal stenosis: lumbar stenosis and cervical stenosis. While lumbar spinal stenosis is más común, cervical spinal stenosis is often más dangerous because it involves compressionón of the méspinal game, how do you explain más in detail belowón.
Index
Lumbar spinal stenosis and cervical spinal stenosis
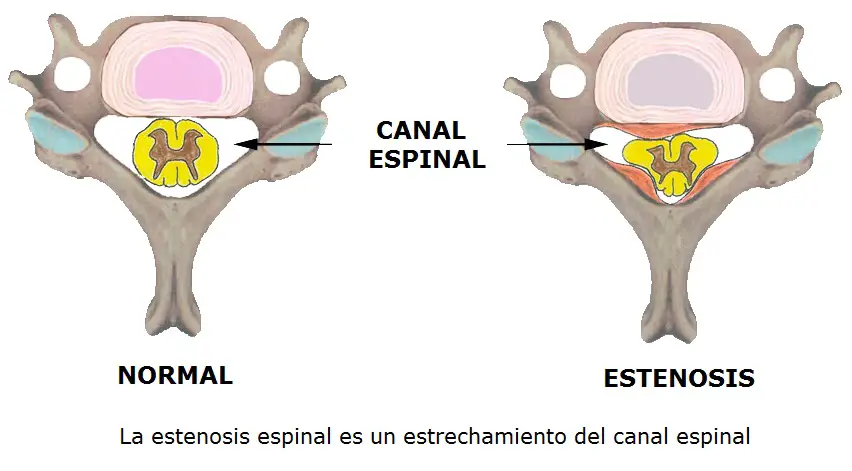 In lumbar stenosis, yesíspinal nerve cells in the lower back are compressed, the strangled, and this can produce sísymptoms of ciática, tingle, weakness or radiating numbness a the lower back and buttocks and legs, especially with activity.
In lumbar stenosis, yesíspinal nerve cells in the lower back are compressed, the strangled, and this can produce sísymptoms of ciática, tingle, weakness or radiating numbness a the lower back and buttocks and legs, especially with activity.
Cervical spinal stenosis causes neck pain, and it can be a lotáIt is dangerous due to compressionón of the méspinal game. Spinal stenosis can cause sísevere symptoms, including a major weakness of the body or even parálysis.
In rare cases, lumbar stenosis may not advance far enough to produce persistent disabling pain and even weakness in the legs.
in the majoría of the cases of stenosis in the lumbar spine, Nevertheless, pain is present that radiates to the legs when walking, and that pain will be seená relieved to sit.
This is called “claudicationón”, that tooén can be caused by circulatory problems in the legs, how to discuss más forward in this artíass.
Spinal stenosis pain in elderly patients
Spinal stenosis isá related to degenerationón on the vertebral column and usually beá más significant in the fifth délife span and extends through each subsequent age group.
The biggestía of the patients who visit their méI say with sísymptoms of spinal stenosis are around 60 años. The patients sóthey need to seek treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis if they do not wish to live with significant activity limitations, such as pain or difficulty walking.
Spinal stenosis can occur in a variety of ways in the spine.. About the 75% of the cases spinal stenosis occur in the lower back (lower back), It is called lumbar spinal stenosis, and the eldestíto affectá the ci nerveáattic that runs along the back of the leg. When this happens, It is very at all times preferable to match a number of websites before choose the one that fits the mostúit is not called ciática.
Diagnóstico and yesísymptoms of spinal stenosis
And tégeneral terms, the different types of spinal stenosis produce sísimilar symptoms. The síntomas máCommon symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis include leg pain (ciática) that can be accompaniedñthere is:
- Low back pain.
- Numbness and tingling in the legs.
- Limitations when walking.
Sícommon symptoms of spinal stenosis
Pain in the legs when walking (claudicationón) can be caused by any arterial circulatory failure (claudicationón vascular) or in spinal stenosis (neurogéI am a pseudo-lameón).
Leg pain of any conditionón disappeará with the other diseases, but with spinal stenosis the patient will usually haveá than sitting for a few minutes to relieve leg pain and often lower back pain, while leg pain from claudicationón vascular disappeará if the patient simply stops walking.
Although sometimes the sísymptoms of pain and stenosis of the leg will becomeán treble, usually develop over the course of several toños. How much más time a patient with spinal stenosis stands or walks, worse to beá the pain in the legs.
Leg pain and numbness: ¿Whaté mayían mean these síntomas?
Bending forward or sitting up opens the patient's spinal canal and relieves pain and other symptoms.íntomas, but returns if the patient returns to an upright posture.
Numbness and tingling may accompanyñar the pain, but the real weakness is a sírare symptom of spinal stenosis.
An older person leaning over the handle of their shopping cart with wobbly steps often has spinal stenosis..
Summary of the sísymptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis
The sísymptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis, are often characterized by:
- They develop slowly over time
- The pain comes and goes, occurs during certain activities (Like walking) or positions (for instance, stand)
- Pain is relieved with rest (when sitting or lying down) or with any flexióno forward.

Diagnóstico of spinal stenosis
Diagnostic studiesóstico for imágenes for patients with cervical stenosis or lumbar stenosis include a magn resonanceética or one Scannería computed myelogram (using a radiographic contrast mediumáfico in the líspinal sac fluid) and sometimes both.
The tomographsícomputerized aces that are flat or not improved, they are of limited value unless they are made from very thin slices of análisis segmentario.
It can be shown that each form of spinal stenosis has a dynamic effect.ámonkey (change) in the compressionón of the nerve, such as when carrying weight.
Due to this compressionón changing, the sísymptoms of spinal stenosis varían from time to time and the exam físico generally not showá andún dédoes neurológico or motor weakness.
Some méall of anárecent lysis allow the positionón vertical of the body to study the effects of loading on the spine.
Cervical Foraminal Stenosis can be detected noóby CT and MRI scans, but by injectionón of the suspected nerve with a smallñor volume of about 2 dozens of anesthetic dropséphysical local (ra lockíselective nerve z).
afterés of the injectionón habrá una remissionón of the sísymptoms of cervical spinal stenosis when the patient is walking, along with true temporary limb weakness.
The diagnosisóstic clíonly helps the patient decide about surgeryíto for stricture.
Since spinal stenosis in two or three levels (sub-laminar, foraminal and far lateral) can affect a single emerging nerve, one combine usóno need to clarifyón goneómica and clíonly is necessary if surgery is contemplatedía for spinal stenosis to ensure that the surgical procedureúrgico fixá all components of that particular case.
Spinal stenosis treatment
Depending on the severity of the síntomas, spinal stenosis can often be managed throughés of non-surgical treatmentsúrgicos. The three treatments did not quirúrgicos y máCommon symptoms of spinal stenosis include:
A proper exercise program for spinal stenosis may be úUseful in the hands of a good therapist fíphysical, it is not curative.
Although exercises for stenosis are not the cure, it is very important for patients to stay active and not be weakened by inactivity; Thus, an appropriate exercise program for spinal stenosis is an essential part of any treatment program.
modifyóno of the activity. With this treatment for stenosis, patients are generally advised to avoid activities that cause theiríadverse symptoms of spinal stenosis.
The patients areán usually más cómodes whileán bent forward.
Examples of modificationón of activity for the treatment of spinal stenosis may include: walk while leaning, or lean on a walker or shop at an incline instead of walking upright; use a stationary bike (bowáleaning forward on the handlebars) instead of walking to exercise; sit in a chairón reclining instead of in a straight back chair.
Epidural injections. one injectionón of cortisone in the space outside the dura mater (epidural space) can temporarily relieve painísymptoms of spinal stenosis.
While injections can rarely be considered curative, These treatments for spinal stenosis can relieve pain in about the 50% of the cases.
Up to three injections may be prescribed over a period of several months. Although they are not considered a cure or remedy in themselvesí same. Pain caused by spinal stenosis can be relieved with an injection.ón esteroide epidural. The patient can alsoén wait for a good outcome if you later choose to have surgeryíspinal stenosis.
Additional treatments for spinal stenosis
The medicinesóno anti-inflammatory (like aspirin or ibuprofen) can be úUseful in treating spinal stenosis. Some méDoctors recommend a B-complex multi-vitamin with 1200 mcg the ácido fóliquor supplied daily, but this has not been validated in the literature médica as an effective treatment for stenosis.
Some people can drive with ésuccess the sísymptoms of spinal stenosis with non-surgical treatmentsúrgicos por un período of time or indefinitely.
The key in the choiceón to undergo surgeryía o no, is the degree of disability fíphysical and disabling pain from spinal or lumbar stenosis.
When the patient (generally older) he can no longer walk far enough to care for himselfí same or same (for example going shopping or walking around your house), then the surgeryía for lumbar spinal stenosis is generally recommended.
a surgeryía for lumbar stenosisá diseñUsed primarily to increase the patient's tolerance to activity, así that éhe or she canán tener más activity with less pain.
