Achondroplasia is a genetic diseaseética, causada por la mutationón del gen FGFR3. It is characterized by the shortening of the extremities in relation toón with the normal length of the trunk. East á based on a declineón of bone growth and chartílagos. Hereí we will show you their characterísticas, Causes, síntomas, diagnóStatic and frequent treatments.

dwarfism isá closely related to achondroplasia, people who suffer from this conditionón have faced each other over the yearsñthose with discriminatory treatment. Nevertheless, Others have made their way into the world of film and television.ón, as an example of this we have actor with achondroplasia Peter Dinklage from the series Game of Thrones.

Index
Characterísymptoms of achondroplasia
It is type of dwarfism It is characterized by the decreaseóno tissue growth óseo (less than 130 cm high). The biggestía of the patients present deformaóno of the spine, macrocephaly, saddle nose and waist lengthóbad limbs.
Achondroplasia if presented with más frequency in women. At birth, the niñthose with this pathologyía have reduced growth and unusually large head circumference. some characterít sticsípicas presented by patients with achondroplasia are:
 Short arms and legs
Short arms and legs- Eyes wide apart
- hearing problemsóno visitón
- Flattened nose
- Large head with convex forehead
- Spinal disorders
- Dental problems
- Weakness in muscle tone
- Bowlegged
- Trident hand
- Overweight
- Delayed motor skills
Causes
Achondroplasia is caused by a mutationón in the gene that controls the productionógrowth factor receptor n. This affects the ossificationócorrect card numberíepiphyseal lake, which isá associated with the bones of the cráneo and tubular bones of the limbs. The receptor is believed to be found in all ágrowth areas of the skeleton.

There are several factors that contribute to the onset of the disease, among them isán:
• parents between 35-40 años, especially the father. It is often found in men afterés of the 40 años.
• The presence of achondroplasia in the parents. In this case, the probability that the childñor inherit this defect is from 50%.
Síntomas
Patients with achondroplasia may have different síntomas, within which isán: neurológicos, respiratory, auditory, engines, cognitive and orthopétips. Además of these símain symptoms, there may be other associated manifestations, not with the underlying disease, but with its consequences. For instance, cifosis of the neck and spineácat.
In adolescence, there are often complaints of pain in the legs and lower back. This is caused by the pressureón of the spinal canal in the médrama. If no special measures are taken, soon to giveá place on parálysis of the legs.
Sometimes, I received themén born with achondroplasia die during sleepñO. Presumably, this is due to pressureón on the méspinal cord at the top, that prevents the proper work of the órespiratory organs.
Síntomas neurológicos
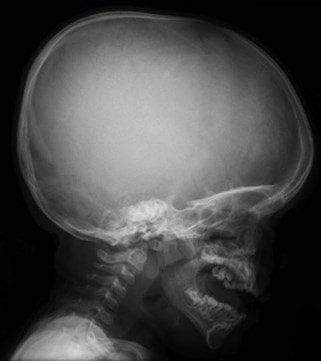
One of the main síntomas neurológicos is the insufficient development of the base of the cráneo and the spinal canal, what can cause compressionón in the médula and the medulla raquídeo. To circulateón of líquido cefalorraquíGod could be affected.
Compressions can cause abnormal reflexes and muscle weakness in the legs., neuronal manifestationsóclear symptoms of achondroplasia. The narrow shape of the channels at the base of the cráneo can cause poor coordinationón and weakness in the throat or in the múbreathing circles.
I understood herón of the méspinal game (spinal stenosis) can cause sísymptoms in the form of a tired back, pain, numbness, tingling in the legs, parálysis and urinary incontinence.
Sírespiratory symptoms
Insufficient development of the respiratory tract in patients with achondroplasia, lead to appearóNo sleep apneañO. Frequent enlargement of the amíglands and adenoids can aggravate these abnormal pauses in breathing.ón.
The tórax can be narrow, causing shortness of breath, así as the decreaseón the ability to exhale the diócarbon dioxide. All these breathing problemsón decrease when the niñor grow and seeíairways become más wide.
Síauditory symptoms
The reduced space between the oíinternal ear and pharynx causes increased risk of inflammationón acute and crónica del oífrom the middle (otitis media). This can cause a decreaseón from hearing aidsón and sometimes slow development of speech.
Símotor symptoms
The development of motor skills is delayed by the muscle weakness present in children.ños con achondroplasia, sísymptom that improves with age. La retentionón of the head begins only until the 6-7 months old. Fine motor skills are affected by anatomy.íby the hands.
The niñThose with achondroplasia begin to walk around the 18 and 30 months in majoría of the cases. This delay is the result of a combinationón muscle weakness in the legs and knee joints. Además, an unusually large and heavy head that causes difficulty in balancing.
Sícognitive symptoms
Language development is often delayed for several months. This may be the consequence of deterioration caused by períears of infectionsóunique of the orído and the possible affectón of the cranial nerves in the functions and movements of the pharynx.
Other factors that can affect speech, are skeletal facial disorderséticos, like the tall and narrow palate. Además, of the restrictionón of mouth space caused by increased amíglands and adenoids.
Síntomas orthopétips
 The weakness of the músculi of the trunk, together with an alterationóno of the vévertebrae can cause the formationón of kyphosis that is generated in the first toñthe life. Persists in the 30% of the childrenñand in some cases it progresses.
The weakness of the músculi of the trunk, together with an alterationóno of the vévertebrae can cause the formationón of kyphosis that is generated in the first toñthe life. Persists in the 30% of the childrenñand in some cases it progresses.
This kyphosis is mábe noticeable whenán sitting and almost disappears when the childñor with achondroplasia lies on his stomachódry. This is degenerationón is usually smallñto in the majoría of the cases.
Joint problems are often common, mainly in the arms. It is evident when the childrenñyou experience difficulty in extending them. People with achondroplasia often have weak ligaments and cájoint capsules.
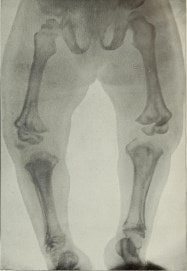
The gait or way of walking can be affected by anatómonkeys of the pelvis and hips, weakness of the múmuscles of the back and abdomen. The DéJoint problems in the knee and ankles together with incorrect growth of the tibia cause deformities of the lower extremities.
Diagnóstico
The diagnosisóStatic can be made at birth based on certain characteristicsít sticsípicas of achondroplasia or from the úwomb throughés of a selection testón genética. In some neitherños, these characterífan sticasíphysiques are less obvious at birth, and approximately the 20% of the childrenñare diagnosed náit's late, during the first toñthe life.
The diagnosisóPrenatal static is possible if a normal ultrasound indicates achondroplasia or if a mutation has been established.ónot in the family. Nevertheless, skeletal disorderséticos become más evident during the second trimester.
Some méall to diagnose achondroplasia, include evaluations fíneurol physicsócool, genéethics and radiolócool. If no studies have been conducted during pregnancy, then the diagnosisóStico can be done afterés of birth.
The evaluations fíphysicals are made based on the appearance of the patient, where facial and body features are decisive. The specialist assessá head circumference, limb length and proportionón corporal a través of growth meter tables.
A DNA test can show the mutation.ón in the FGFR gene 3. X-ray tests más used are those of cráneo, tórax, spine, pelvis bones and joints. that can demonstrate disproportionón between the brain and the cráneo, deformationón in the sternumóno and ribs, cifosis, change of the bonesíacos, joint deformity, among others.
Frequent treatment
Treatment of achondroplasia for a recoveryócomplete n of patients is impossible. At an early age, conservative treatment is carried out, aimed at strengthening theúdogs, preventing limb deformity.
small patient therapyñthose with a diagnosisóachondroplasia has as úsole objective to mitigate complications múmultiples. Treatment for achondroplasia is symptomatic.ático. East á aimed at the eliminationón of sípain syndrome through medication.
SpaghettiéThere is no therapy to minimize complications and their consequences. For these purposes, several m can be usedéall: using growth hormone, a través of the strengthening of the músculos and preventionón of the posterior curvature of the extremities.

La rehabilitationón, the massage, therapeutic gymnasticséutica, the use of shoes and corsés ortopéspecial sayings, preventionóno obesity, operations like: osteotomía, laminectomíto and elongation of the extremities. They are other ways to decrease the sísymptoms of achondroplasia.
