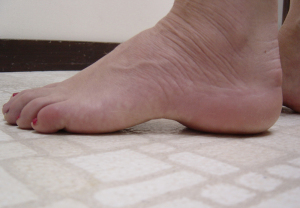
The niñThose with cavus feet have arches that are much larger.ás higher than usual. Often, her heels point inward, and all of your toes flex.
The niñthose with cavus feet have trouble finding shoes that fit. The top and center of your feet may be sore, and develop thick calluses under the ball and on the outer edges of the feet.
Due to their high arches they make their ankles turn out a little, the niñThose with cavus feet may feel that their ankles areán about to meet. Sometimes they sprain their ankles over and over again.
Index
Pes cavus in niños
The niñthey are rarely born with this problem. Instead, pes cavus usually develops slowly during the first 10 añthose of life.
In most of the cases, the niñyou develop pes cavus because you have a nerve or muscle disease. The disease causes some of the músculos sean más débiles than others. These múunbalanced muscles work unevenly, causing the arch to rise and other signs of pes cavus.
An inherited disorder called the disease Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) is the causeás común of the hollow foot. But there is a long list of disorders that can cause the problem..
For instance, the niñthose who have muscular dystrophy (DM) and the spine bítrust, for instance, son más more likely than others to develop pes cavus in both feet. In other words, a group of inherited disorders of the múdogs can cause them to become very débiles.
Además, cavus foot tooén can affect only one foot, What is más común in neitherñChildren with nerve damage to the legs or wristéspinal cord or in the múscules of his legs. Other conditions that make it máit's likely that a niñor develop pes cavus are the poliomyelitis, the parálisis cerebral and tumors from méspinal game.
The síntomas of the hollow foot
He símy youthás obvious cavus foot is a very high arch or arched foot. People with cavus feet alsoécan not present:
- Calluses on the sides, heels or balls of your feet
- Bent toes (hammer toes)
- Well flexed fingers (claw toes)
- Pain when walking or standing
- Tendency to twist the ankles
Diagnóstic of the hollow foot
First, we ask the childñor standing while your feet are examined for signs of pes cavus. Because pes cavus tends to run in families, frequently the médoctors ask to examine alsoén the feet of parents and other family members.
Spaghettiéshould not be checked:
- Leg strength, the ankles, your child's feet and toes, since pes cavus often comes along with diseases that make the múdogs débiles
- Spinal column, to make sure it is flexible and the correct shape
- The reflections of the childñor on the legs and belly (abdomen)
- One must ask if heñor have had problems controlling bowel or bladder movements. By úlast, X-rays are takeníace of the back and the feet of his son.
Once it is known that the niñor do you have a cavus foot, you should start looking for the cause of the problem. Your child may need to have several tests to find the cause of pes cavus., including:
- An electromyogram and conduction velocityón nervous (EMG / NCV).
- Blood test for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT)
- IRM (Magn Resonance Imageética) of the spine and brain.
The exesámenus to diagnose nerve and muscle problemsúI am afraid of the dogsé so well the nerves conduct the impulses theéctricos that control the múdogs, and alsoén help the métell them to evaluate the dayñthe nervous.