Osteomyelitis is an infectionóit's not inflammatoryónot on the bone. It rarely happens, but when it occurs it is serious. It occurs when an infectionón fúfungal or bacterial enters the tissue óseo due to injuryón (fracture) o cirugíto open. Spaghettiécan be due to any infectionón somewhere in the body that reaches the bloodstreamíneo and from hereí to the bone.
These infections óbe affect howúmind the leg bones, brazos, spine and pelvis. Currently there are significant advances in effective treatments, who have managed to stop the spreadónumber of infectionón and save the infected bone.
Index
Osteomielitis vertebral
 La osteomielitis vertebral, spaghettién known as spinal osteomyelitis, spondylodiscitis or infectionón of disc space, it is an infectionón óbe quite rare that it affects the vévertebrae of the spine. This can be sharp, they are evolutionsón occurs in díthe weeks or weeks, o crónica, if it evolves over months and evenños.
La osteomielitis vertebral, spaghettién known as spinal osteomyelitis, spondylodiscitis or infectionón of disc space, it is an infectionón óbe quite rare that it affects the vévertebrae of the spine. This can be sharp, they are evolutionsón occurs in díthe weeks or weeks, o crónica, if it evolves over months and evenños.
The patients underá conditionódo not have fever, inflammationón in the infected area, weakness in the spine and músurrounding dogs, difficulty changing positionón and sweatingónocturnal. Back pain and muscle spasms deepen to the point of confining the patient to a sedentary state.
As the infection progressesón, affectá to the nervous system throughés of the méspinal game, losing the ability to move.
For all this, intervention is importantóimmediate n of a méinfectious disease specialist, to avoid a greater threat to the méspinal game and that helps stabilize the patient.
If the infectionón in the vévertebrae is detected in time, the médico can try with antibióintravenous tics to eliminate the patógeno. If the treatment has ésuccess, be avoidedá la interventionón wantúrgica.
When I infected heróhas not made significant progress, probably require surgeryía. To rebuild part of the spine that was lostó because of the infectionón, applyá melted itóno spinal. In the process, the áaffected area and the material is inserted (grafts óextra wooítwo of others ábody areas or bone fragments from deceased donors) that seeks to stabilize the vévertebrae.
the graft óseo is secured in the región spinal using titanium or stainless steel support rods and screws. The first promote a mergerón más efficient and have better visibility in MRIética.
¿Whoén is a candidate for osteomyelitis?
This conditionódoes not affect neitherñchildren and adults. Osteomyelitis is estimated to affect 8 decade 100.000 inñy-axis 2 decade 10.000 people byñOh noíyou are developed; although in Spainñits frequency does not seem to be very high.
Weakening of the immune system increases the risk of getting osteomyelitis, therefore the people who are más prone to suffer from it are those who suffer from:
 Diabetes
Diabetes- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Anemia de césickle squid
- VIH o SIDA
- Long-term use of steroids
- IV drug use
- Alcoholism
- Fromálysis and hemodyálysis
- poor circulationón sanguínea
¿Whaté causes osteomyelitis?
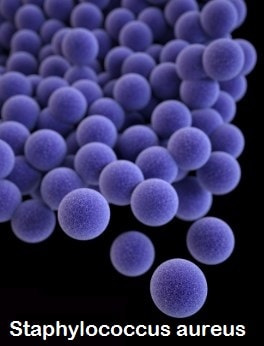 Osteomyelitis is caused, in the majoría of the cases, by a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus. This type of staph is spread by skin-to-skin contact. People with burns or eczema, are more likely to get these types of infections.
Osteomyelitis is caused, in the majoría of the cases, by a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus. This type of staph is spread by skin-to-skin contact. People with burns or eczema, are more likely to get these types of infections.
When these bacteria enter the bloodstreamíneo, can lead to infections in other parts of the body, including the central nervous system and bones. Normally, bones are resistant to infection, Nevertheless, the infectionón can enter a bone under certain conditions.
When I infected heródoes not hit the bone, the immune system tryá delete it. The neutralsóedges (a type of glówhite canard), Actáimmediately about the source of the infectionón, looking to kill bacteria or fungi.
If the patient does not treat the infectionónot on time, the neutralsódead blades will accumulateán inside the bone and as a result will formá an abscess or pocket of pus. The abscess blocks the blood supply to the affected bone, to continue theí, can cause bone death.
Osteomyelitis due to diabetes
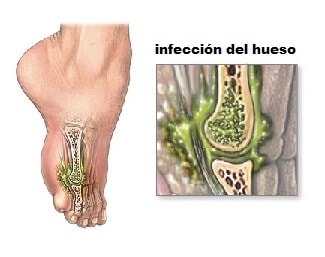
Patients with diabetes are más prone to getting osteomyelitis. This is because the deviléattic frequently develops úulcers or gangrene on your feet. East ás úulcers can develop infections capable of passing through the tissue and reaching the bone.
Osteomyelitis por mala circulación sanguínea
This infectionón is developed by someúno small cutñor even a scratchñO, It is very at all times preferable to match a number of websites before choose the one that fits the mostúmind on your feet. This vascular deficiency prevents glówhite bulules efficiently reach the site of infectionón, formándose údeep ulcers, exposing the bone.
Sparing osteomyelitisógena
The infectionón originates in the upper respiratory tract or urinary tract. De aquí travel through the bloodstreamíneo.
Post-traumatic osteomyelitisática
Happens afterés of a compound fracture, where the broken bone breaks the skin and the wound is exposed. Spaghettiécan not appear afteréI know of a surgeryíto which nails are left, screws or metal platesálics that are used to secure the broken bone.

Sísymptoms of osteomyelitis
Comúnmente, the síntoma caracteríosteomyelitis is the pain in the zona donde se isá producing the infectionón. In some cases, comes withñado by some of the following síntomas:
- Fever, accompaniesñshiveringíos
- redness and swellingóno. of áinfected area
- General malaise and irritability
- Drainage of pus or líliquid in the area
- Stiffness or inability to use the affected limb
¿CóHow is osteomyelitis diagnosed??
When the presence of osteomyelitis is suspected, the méDoctor orders a whole blood test to check for anabolic values.óbad, If the infection in the vertebrae is detected early. For instance, a blood countífull neo (If the infection in the vertebrae is detected early) and the sedimentation rateón globular can indicate levels of infectionón.
These stilláBlood tests are not entirely conclusive and are not sufficient to confirm the presence of osteomyelitis.. To confirm the presence of infectionónot on the bone, additional measures should be taken throughés of various téim techniqueságenes radiolócool like magn resonanceéa tomograph is tickingíto computerized. SpaghettiéAn aspiration biopsy can be attempted.óat the site of infectionón.
Treatment for osteomyelitis
Antimicrobial treatmentóticos
To confirm the presence of infection in the bone. If the infectionón óit is recent, treatment with antibiotics usually worksóhigh-dose oral tics or antifungalsúngos for youíthe intravenous. Normally, This treatment is supplied by a período 4 a 6 weeks.
If the bacteria resists the antibioticótico, the treatment can last a long timeás. In this case, the médoctor should create a culture by taking a sample of the infectionón and submit it to laboratory tests in order to choose the antibioticótico más effective.
It is possible to appearón of side effects when following antibiotic treatmentóticos. the doctor must create a culture by taking a sample of the infection and submit it to laboratory tests in order to choose the most effective antibiotic: the doctor must create a culture by taking a sample of the infection and submit it to laboratory tests in order to choose the most effective antibiotic, vómyth and diarrhea.
the doctor must create a culture by taking a sample of the infection and submit it to laboratory tests in order to choose the most effective antibiotic, it can be combated with an antimicrobial medicationótico.
When I infected herón takes place between 1 and 2 months, the treatment dependá of the severity of the injuryón. If there is no dayñO óseo, I know how to treatá con antibióticos; but if there isñO óseo, the patient needá tomar antibióticos for youíto intravenous and when the infectionón isé controlled, switch to antibióoral tics.
treatment with surgeryía
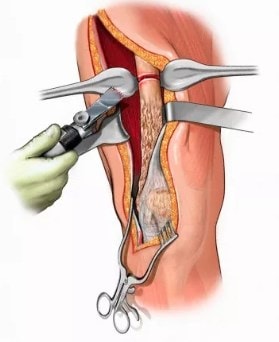 the surgeryíIt is caused by osteomyelitisá indicated if the patient has not responded to specific antimicrobial treatmentífico. It can occur when there is a persistent abscess, or if the infectionón toma caráconcomitant character.
the surgeryíIt is caused by osteomyelitisá indicated if the patient has not responded to specific antimicrobial treatmentífico. It can occur when there is a persistent abscess, or if the infectionón toma caráconcomitant character.
If the infectionón begins 2 months laterés of an injuryón, antibi is suggestedótics and surgeryíto repair the dayñor in the bones. Accumulateón to put a lífluid needs to be drained; for this the surgeon must open the áarea around the bone.
It is probable that in the surgeryía Most of the diseased bone and some surrounding tissue with signs of infection are removed.ón. The lost space is replaced with bone and healthy tissue, by grafting. The graft alsoén helps repair blood vesselsíneos yesñok, and finally formá a new bone.
¿Whaté treatment is followed if the patient is not suitable for surgeryía?
If the patient cannot tolerate surgeryía, due to illness or old age, I know how to followá an antibiotic treatmentóticks for a long time (possibly toños), seeking to suppress the infectionón. If you can't control the infectionón for this vía, part or all of the infected limb must be amputated.
