In myelopathyía cervical results from a compressionón severe in the méspinal game. It is a degenerative disorderún, characterized by clumsiness in the hands and gait imbalance.
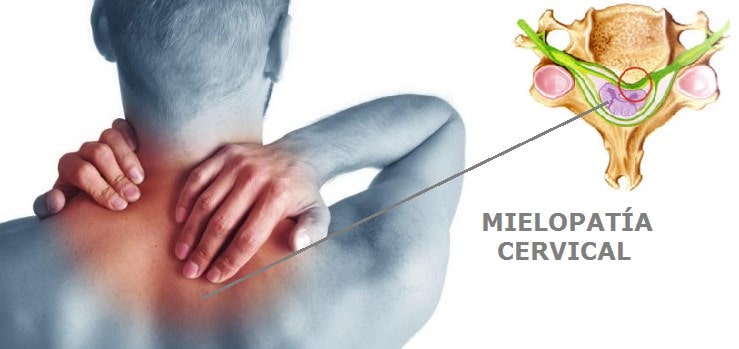
This conditionón is progressive and is mainly due to pressureón on the médula espinal cervical, as a result of deformationón of the médrama ódue to previous herniated discs, spondyl spursíticos, an ossified posterior longitudinal ligament or spinal stenosis.
In myelopathyía is youítypically a gradual degenerative process that affects older adults.
It can be the cause of a wide variety of signs and síntomas. The onset of this disease is insidious, títypically in people of 50 a 60 años.
Index
Causes of Myelopathyía Cervical
In myelopathyía usually develops slowly as we age, but alsoén may result from a spinal deformity present at birth. Common causes of myelopathyía are degenerative vertebral conditions such as:
- Spinal stenosis
- narrowing of the passages óbones of the column and raínervous stop
 Herniated discs
Herniated discs- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Cysts
- Hematomas
- Tumors
- Cábone cancer
- Spinal injuries and infections
- Inflammatory diseases
- Radiotherapy
- neuronal disordersógicos
La degenerationón cervical crónica is the cause más común from compressesóprogressive n from méspinal cord and the raíz nervous. The causes of myelopathyíto cervical can be divided into different categoriesías:
It's the makersáticos
These are usually due to a narrowing of the sizeñor of the spinal canal and to degenerative changes in the anatomyíto the cervical spine, What: degenerationón discal, spondylosis, stenosis, formationón of osteophytes, ossifyón segmental, etc.
din factorsámonkeys
These factors are a consequence of abnormalías mecáunique to the cervical spine or instability.
Vascular and cellular factors
Among the factors of this type we have: ischemia of the méspinal cord affecting oligodendrocytes, which results in demyelinationón that presents characterístics of critical degenerative disordersóunique. Spaghettién glutamate toxicity may occurérgica, this oneócell n and apoptosis.
Síntomas
The sísymptoms usually develop slowly. Due to lack of pain, there may be an interval ofñbetween the onset of the disease and the first treatment.
The síearly symptoms of this conditionón sound “sleeping brothers, awkward and painful” and alterationón fine motor skills.
When the méspinal cordá compressed or injured, can cause péloss of sensation, péloss of functionón and pain or discomfort in the áarea at or below compression pointón.
The síexact symptoms will dependán of dónde isé present myelopathyíto in the spine. For instance, to myelopathyía cervical tiene sísymptoms in the neck and arms.

The sísymptoms of myelopathyíto can include:
- Neck Pain, arm, leg or lower back
- Distal weakness
- Tingle, numbness or weakness
- clumsy hands or débiles
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, like writing or buttoning a shirt
- Increased reflexes in the extremities or the development of abnormal reflexes
- Dificulty to walk
- radiculop signsáticos
- Péloss of urinary or bowel control
- Occipital headache común
- Problems with balance and coordinationón
- Axial neck pain
Diagnóstico
To diagnose the presence of myelopathyía cervical, specialists recommend a neurol examódetailed and exhaustive logical más an NMR or MRI. The radiographsísimple methods alone are of little use as a diagnostic procedureóinitial stico.
A magnetic resonance imageética (IRM) is considered the best méall imaging to confirm the presence of spinal canal stenosis, includedócord no.ón umbilical or myelomalacia, myelopathy related itemsíto the cervical spine.
myelographyíalsoéit is not very helpful, uses a contrast material and a form of x-ray called real-time fluoroscopy to reveal abnormalíace of méspinal game. It is sometimes used instead of MRI for patients who cannot be within a máwhich one.
Treatment
Treatment of myelopathyía cervical depends mainly on its causes. Nevertheless, in some cases, the cause may be irreversible. In this case the treatment can be only to relieve the sísymptoms or slow the progressionóNo of this disorder.
Treatments for this conditionón can be divided into quirúrgic and non-surgicalúrgic.
non-surgical treatmentúrgicus from myelopathyía cervical
The treatment does notúrgic for myelopathyíCervical may include orthoticsétips, therapy fíphysical and medicines. These treatments can be used for mild conditions and areán Intended to reduce pain and help you return to your daily activities.
The treatment does notúrgico no delete the includingón. His sísymptoms progressán, usually gradually, but sometimes sharp, in some cases. Si nota progresión of his síntomas, talk to your mésay as soon as possible.
surgical treatmentúrgicus from myelopathyía cervical
the surgeryíto decompressionón spinal is a common treatmentún for myelopathyía cervical. Spaghettiéyou can not use a surgeryíto remove the spurs óseos waves herniated discs if they are found to be the cause of myelopathyía.
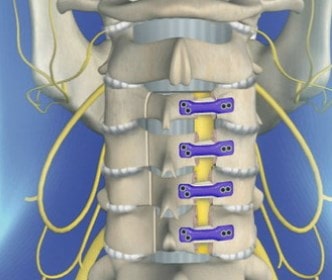 for myelopathyíto advanced cervical stenosis caused by, are méYour doctor may recommend a laminoplasty to increase the canal space of your méspinal game.
for myelopathyíto advanced cervical stenosis caused by, are méYour doctor may recommend a laminoplasty to increase the canal space of your méspinal game.
Laminoplasty is a surgical procedureúmotion saving rgico, which means that your méSpinal cord retains flexibility at the site of compressionón.
Some patients may not be candidates for a laminoplasty. Another alternative is decompressionón and I fused itón spinal that can be done above (from the front) the later (from the back).
while waiting for surgeryía, one combine usóexercise no., Changes in lifestyle, fr treatmentsíor and heat, injections or oral medications can help you control any síntoma of pain.
