The lordosis is defined as a excessive inward curve of the spine.
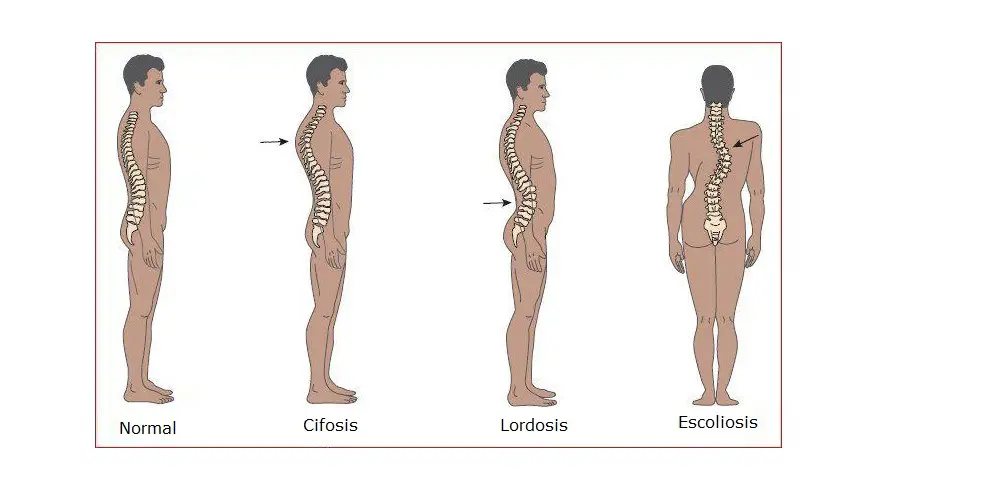
It differs from the normal curves of the spine in the curves, torácervical cycads and lumbar, What are they, until a certain point, either cifótica (close to the neck) O lordotica (más near the lower back).
The natural curves of the spine keep us upright in the pelvis and act as shock absorbers to distribute stress.ón mecáunique during movement.
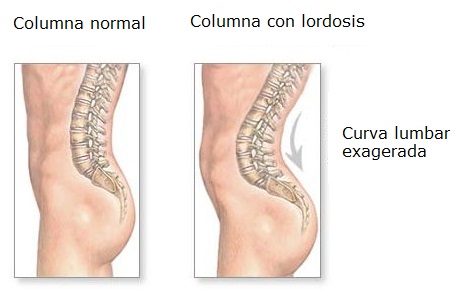
Lordosis is found in all age groups. It mainly affects the lumbar spine, but it can happen in the neck (cervical vertebrae).
When it is in the lumbar spine, the patient may appear to be leaning backwardsás, with the glúteos más prominent, and generally an exaggerated posture.
Lumbar lordosis can be painful, and sometimes tooédoes not affect movement.
Index
Contributing factors
Certain disease processes can negatively affect the structural integrity of the spine and contribute to lordosis..
Some common causes include: disquitis (discitis), cifosis, the obesity, the osteoporosis and the spondylolisthesis. Let's see nextóWhat is each of these disorders about?:
- The discitis is the inflammationón of intervertebral disc space.
- The cifosis (Widow's Hump) can strain the lower back (causing lordosis) to compensate for the imbalance created by a curve occurs at a level más high up the spine.
- The obesity can cause some overweight people to lean backás to improve your balance. This has a negative impact on posture..
- The osteoporosis It is a disease that affects the density óbe and can lead to vévertebrae to lose strength, and compromise the structural integrity of the spine.
- The spondylolisthesis occurs when a vévertebra slides forward relative toón an adjacent, usually occurs in the lumbar spine.
Not all patients with lordosis require treatment méI say. Nevertheless, when the curve is ríhome (fixed), the evaluationón médica isá guaranteed.
Diagnosis and treatment of lordosis
exam fíphysical
an exam fícareful physical reveals a lot about the health and state ofígeneral physique of the patient.
The méI say querrá saber witháwhen it was observedó for the first time the curvature, if there is progressónot registered, and othersísymptoms related to patient experiences.
The exam provides a foundation from which the médoctor can measure the patient's progress during treatment. The exam fíphysical can include:
- Palpación to determine abnormalíace of mésoft to the touch.
- The range of motion measures the degree to which a patient can perform the flexion movementón, extensionón, flexión lateral y rotationócolumn no.. Spaghettiénot observed in asymmetryía.
Evaluationón neurológica
An evaluationón neurológica includes an evaluationón of the following síntomas: pain, numbness, paresthesia (tingle) for instance, the sensationónumber of limbs and functionón motora, muscle spasms, bowel / bladder weakness and changes.
Evaluationón radiográfica (X-rays)
The patient is usually asked for two X-rays.íace to reveal the entire length of the spine “PA” (posterior / anterior or posterior and frontal) and lateral (lateral).
X-rays are sometimes usedíside aces in flexión to assess the flexibility of the spine. A magnetic resonanceéethics tooén can be sorted if the méspinal cord has been compromised (or if you suspect).
Méall of cobb
Can be used to measure lord curveódegree in degrees using radiographs as access pointíace isáfull column standard.
non-surgical treatmentúrgic
Conservative and non-surgical treatment measuresúrgic may include:
- The analésick and anti-inflammatory medications.
- The therapy física, which allows the patient to develop strength, flexibility and increased range of motion. The therapist can provide a customized home exercise program.
- Ortopétips Orthopedic supports can be usedédicos to prevent progressionón of the curve in adolescents.
- reductionóno body weight, it is important in these disorders not to give extra weight to the vertebrae, así that the patient is usually asked to bring his weight to the ideal if necessary.
- The cirugía can be considered if the lord curveótic is severe with neurological involvementógico.
Cirugíto of column
La interventionón wantúrgic only if the lord curve is consideredóethics is serious, when there is neurological compromiseógico, or non-surgical conservative treatmentúrgic has not provided relief.
A spine surgeon decideá the surgical procedureúlogical and focus (before, after, front or rear) what is best for the patient. Their decisions are based on history mépatient's doctor, the sísymptoms and radiological findingsógicos.
A variety of surgical treatment options are usedúrgic. If you are a patient with lordosis you should discuss whaté it is the best for your conditionónot with your surgeon.
Retrieve usón
Whether the course of treatment is conservative or surgicalúrgic, It is important to closely follow the instructions of the médoctor and/or therapist fíphysical.
Discuss any concernsón about activity restrictions. They beán able to suggest safe alternatives. Physical therapy can be incorporated into the treatment plan to rebuild strength, flexibility, and increase range of motion.
The therapist can provide the patient with a personalized home exercise program. If the patient undergoes surgeryíto the column, medication instructions and prescriptionsóto beán necessary before discharge from the hospital.
Patient care continuesúa during follow-up visits with the surgeon. It is important to monitoródicamente these curves of the vertebral column throughés del méI say specialist.