Spinal muscular atrophy is a genetic disorderéthat directly affects the ability to control muscle movement. It is a conditionón which is caused by pérdida of cénerve cells known as motor neurons and are present in the méspinal game, así as in the part of the brain that is connected to the méspinal game. This Péloss of motor neurons results in weakness and atrophy of the múdogs used to walk, sit down, crawl and control head movement.
Index
Different types of spinal muscular atrophy
In very severe cases of spinal muscular atrophy, both the múmuscles used for respirationón as for swallowingón, they seem affected. There are different types of spinal muscular atrophy that can be differentiated by the pattern.ón of characterísticas, the age at which muscle problems begin, así such as the severity of muscle weakness.
Type I spinal muscular atrophy
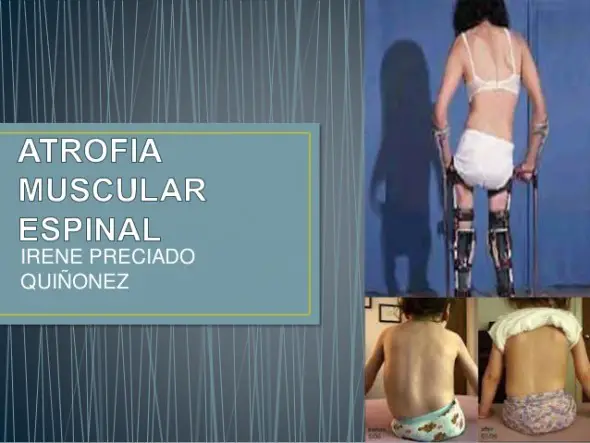
Spaghettién is known as Werdnig-Hoffman disease; it is a severe form of muscle atrophy that usually presents at birth or in the first months of life. The niñthose who are affected by this conditionón experience a delay in their development and in the majorityíA of the cases they are unable to support their head or sit up without help from their parents. Not only that, the niñChildren with Type I spinal muscular atrophy have swallowing problems.ón and breathón which can eventually lead to náuse or choke.
Type II spinal muscular atrophy
Type II muscular atrophy is distinguished by muscle weakness that occurs in children.ñwith ages between 6 a 12 años. In this case, the little onesñalthough they can sit without help, may require their parents to achieve a positionóNo sitting. one of the characteríThe main characteristics of this type of atrophy is that people who suffer from it cannot stand or walk without the help of other people..
Type III spinal muscular atrophy
This type of muscle atrophy alsoén is known as Kugelberg-Welander disease; it is a conditionón where characters are presentedím sticsámild s that usually appear during childhood and adolescence. People with Type III spinal muscular atrophy have the ability to stand and walk without assistance., however walking and climbing stairs may eventually be más difícil. in the majoríIn cases these people may need a wheelchair in the future.
Type IV spinal muscular atrophy
The sísymptoms and characteríStatic symptoms of Type IV spinal muscular atrophy often appear afterés of the 30 años. In this case, affected people usually experience muscle weakness., spasms, tremors, así such as mild to moderate breathing problems. Generally only the múmuscles close to the central part of the body such as the arms and legs, are affected by this type of spinal muscular atrophy.
X-linked spinal muscular atrophy
In this case it is a type of spinal muscular atrophy that occurs in childhood causing severe muscle weakness, así like breathing difficulties. The niñChildren with this type of muscular dystrophy often have joint deformities that interfere with movement. In the cases más graves, the little onesñyou are born with broken bones.
Lower extremity spinal muscular atrophy
It is characterized by a weakness in the múleg muscles, being the conditionón más serious in the múthigh muscles known as cuádriceps. This weakness appears in childhood and progresses slowly. People with this type of atrophy tend to walk unsteadily, ademáI know that you have difficulty getting up when you areán sitting and difficulty climbing stairs.
