The Genu eats O “X legs” it is a conditionón in which the legs areán positioned in a áoutward angle when knees meet.
Conversely, al genu varus or bowed legs it is a conditionón in which the knees remain wide apart when a person isá standing, with feet and ankles together.
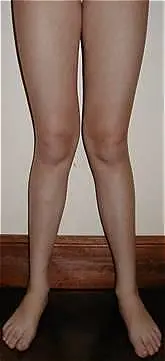
many babieséthey have an inclinationóno yesébilateral tricha of the legs (genu eats), that can persist in the first 1-2 añyears of walking before developing a conditionón of “legs in x” exaggerated.
This transitionón from genu varus to genu valgus may be caused by enlargementóno of the pelvis. The disorder is más dramático to the 3-6 años of age that is known as genu valgus physiológico.
At this time, the áthat's a girlómico can be as tall as 15 degrees of valgus (a deformity in which an anat partómica turns out, far from the límidline of the body to an abnormal degree).
In normal development, the genu valgus then gradually remodels spontaneouslyáin line with the average for adults of 7.5 hallux degrees.
By puberty, the biggestíto the childrenñThey can stand with their knees and ankles in contact (without forcing the positionón).
Index
Questions to ask (By the méI say)
The following points are important aspects of the history when evaluating a child.ñor with a lower extremity problem:
- Reason for consultation. Record exactly what parents refer to in order to provide informationón forecast and discussóno of natural history.
- Historial méI say complete. Include maternal pregnancy, birth and development. Questioning perinatal and motor development events may reveal a diagnosisópair sticálisis cerebral.
- durationón of the problem and progressón. It should be clarified if the problem startedó at birth, the before or afterés to walk. ¿CóHow has the problem changed over the years? úlast months?
- Family background. ¿There is a family tendency of abnormalíace in the lower extremities? AND ¿how often? Knowing the experience and attitudes of parents towards similar problems can help with the discussion.ón posterior.
- ¿Whyé the concernón? know whyé he does not evenñwhere isá in your office or clínica. ¿Is it because of the march or theética? The gait and legs of a childñor are they different from those of an adult. The concernón of parents is often due to a lack of understandingón with respect to maturationóend of the march.
- The signs and síntomas. Ask if there is pain, limp, or if he didn'tñor falls or stumbles frequently.
- Hábits of Sitting. Una torsionón internal tibia is associated withúnmind with which you sit on your feet, while increasing the torqueóFemoral n is associated with sitting in one positionón of “W”.
- Aggravating factors. Torsional deformities become más evident with fatigue.

DiagnóDifferential Stico for Genu Valgus
- hypophosphate ricketsémonkey
- Anterior proximal metaphyseal fracture of the tibia
- Epifisaria dysplasia múmultiple
- Pseudoacondroplasia
Procedure for the investigationóno and treatment
onceón más común for genu valgus o “legs in x” in the niñthe physiol esógica o una variationóno normal development.
The follow-up it is through medicineón serial intercondílea (width between the knees when the feet are placed as close together as possible) and the intermaleolar (the width between the ankles when the child's kneesñor are placed together).
The distances are used to document the resolution.ón answeránea gradual. Yes, I am worth physiológico persist más allá of the 7-8 añyou of age, it is necessary to consult with the orthopedist.
Treatment
For the persistent genu worth, treatment recommendations have included a wide range of options, that go from the restrictionóNo lifestyle and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for reinforcement, exercise programs and therapy física.
In difficult casesíeasy to drive, surgery may be recommendedía. There is no consensus on treatment ógreat. Some surgeons focus on the r itselfótula, what favors the téarthrosc techniquesópricks or reallineóno open.
Nevertheless, if he is worth and misalignedón of the limb is significant, an osteotomy may be indicatedíto corrector.

1 thought on “Genu Valgo”
Comments are closed.