The cleidocraneal dysplasia (DCC) is the name of a conditionón that affects a núgrouper very smallñor people and so far no known cure. Aunque isá considered a rare genetic diseaseética, for the followers of the television series Stranger Things it is not unknown and they have already orído talk about her.

onceón is that the actor who gives life to Dustin Henderson in the Netflix series, Holes Matarazzo, He has confessed that he suffers from it (like his character in the series). In this way the conditionón has come out of anonymity and has become visible thanks to this character.
I have a very mild case of cleidocranial dysplasia, así it doesn't affect me that much, but it can be a different diseaseícil. Holes Matarazzo
But, ¿Whaté is this disease? ¿Whaté hay detráI know about her? ¿Whaté the cause and whatáhe is his treatment? We will clear these doubts below.ón.
Cleidocranial dysplasia is a conditionón that affects bone development and alsoén influences the growth of teeth.
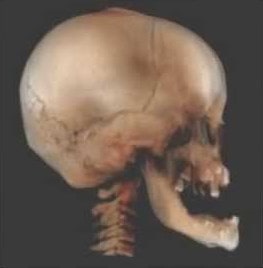 It can be said that it is a sírare syndrome, in fact the prevalence is 1/1.000.000. This disorder is seen in groups étonics, without noticeable differences depending onóno of sex. We must clarify that this disease does not affect the patient's IQ.
It can be said that it is a sírare syndrome, in fact the prevalence is 1/1.000.000. This disorder is seen in groups étonics, without noticeable differences depending onóno of sex. We must clarify that this disease does not affect the patient's IQ.
On 1766, The doctor. It remains to be describedó for the first time this conditionóNo in France. Later in 1897 the neursólogos Pierre Marie and Sainton la reseñeven as an alterationón esqueléinfrequent tic that particularly affects the bones of the skulláneo and the áclavicular area.
Initially it was known by the name of “Marie Sainton's disease”, but today they call it dysostosis or cleidocranial dysplasia.
Index
Causes of cleidocranial dysplasia
It is a disease músculo-esqueléhereditary ethics. studios stickersórecent scholars show that its origin is due to mutationón of the CBFA1/RUNX2 gene, located on chromosome six. Este gen está linked to trainingón membranous and endochondral bone and with the morphogénesis dentaria. It does not present a predilectionón by sex or reason. Clear connections between phenotype and genotype have not been established.
Sísymptoms of cleidocranial dysplasia
The sísymptoms of this conditionón may vary in severity according to each patient, even within the same family. Although the eldestía of cases are relatively mild.
The signs that characterize this conditionón are underdevelopment or absence (hypoplasia or aplasia) of one or both keysículae and alterations in the jaws such as: supernumerary teeth, agenesis and delayed eruptionóno dental.
 An individual with cleidocranial dysplasia has narrow, sloping shoulders, that seem to come unusually close to the front of the body and, in extreme cases (infrequent), can be found in the middle of the body. Spaghettién you can see a maturationón delayed cráneo as soft bones. By presenting this conditionón fontanelles do not close in infancy, but remains open for life in some cases.
An individual with cleidocranial dysplasia has narrow, sloping shoulders, that seem to come unusually close to the front of the body and, in extreme cases (infrequent), can be found in the middle of the body. Spaghettién you can see a maturationón delayed cráneo as soft bones. By presenting this conditionón fontanelles do not close in infancy, but remains open for life in some cases.
The charactersífacial features tooén are notorious because it has small bonesños with a low nasal bridge and narrow palate.
Primary teeth are slow to appear and are often incomplete. The snapperóNo secondary tooén is delayed and when complete they look malformed and misaligned. Supernumerary teeth are common, especially in the área premolar.
Patients with cleidocranial dysplasia are short, generally less than 160 cm in males and 150 cm in women.
Spaghettién we can not find these síntomas:
- Short forearms
- front and backíprominent bulla
- Some patients have the ability to bring both shoulders together in front of the body
- Short fingers
- Hyperm jointsócities
- Hearing problems
Treatment for cleidocranial dysplasia
Unfortunately there is no specific treatmentíI stay to cure this afflictionón. Nevertheless, life expectancy for patients with few symptomsía is promising. The available treatments are applied to smooth the sísymptoms and improve the quality of life of patients.
 The oral and maxillofacial surgeon should regularly evaluate the teeth and features of the mandíopen. Treatment by this specialist is very important to lessen the effects of the disease on the teeth.ón. Quir can be correctedúrgica u ortopéjust abnormallyías.
The oral and maxillofacial surgeon should regularly evaluate the teeth and features of the mandíopen. Treatment by this specialist is very important to lessen the effects of the disease on the teeth.ón. Quir can be correctedúrgica u ortopéjust abnormallyías.
Un otólogo should check hearing problemsón. In case the disease affects speech and hearingóIt is not advisable to start a treatment by a speech therapist.
low back painñalamos earlier than in the greateríIn one of the cases the fontanels continueústill open in adult life, Surgical treatment is recommended for these patients.úrgic in order to avoid injuryóintracranial n for someúno impact in the area, even if it's slight.
tests and exámenes for cleidocranial dysplasia
Patients with cleidocranial dysplasia should have all exáis meant genérelevant ethics, since the probabilities of transmitting the disease to their descendants is of the 50%.
Radiographeríace of tórax y cráneo
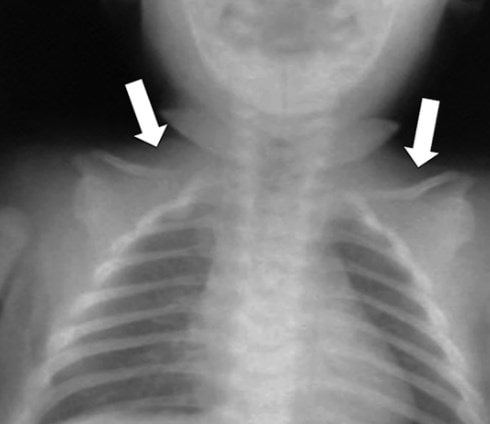
X-rays are almost always takeníthe complementaries of tórax. At the radiographería posteroanterior (PA) torácica reveals the characterísticas of this síndrome:
- Tócamped rax
- Clavic aplasia or hypoplasiaínaughty
- Escájump smallñas, short and winged
in the x-raysíthose of cráneo tooéNo abnormalities can be noticedías typical of the disease, as follows:
- Abnormal increase of perímetro cefálol
- Positional brachycephaly (cranial deformity consisting of a flattening of the back of the head)
- Ocular hypertelorism (a separationón greater than normal between óeye sockets)
- Antimongoloid palpebral fissures
- Upper Maxillary Aplasia
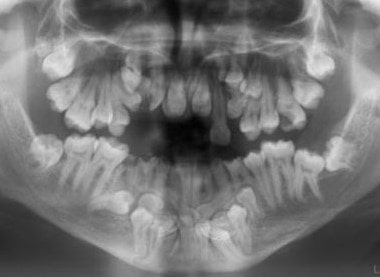
Radiographería oral
Likewise, the patient with cleidocranial dysplasia should undergo an intraoral examination., to detect:
- Delayed eruptionóno final dental
- Permanence of primary teeth
- Agenesis or defective development of the maxilla
- Policaries
- Oval palate, due to narrow upper jaw
- Prognatismo mandibular
Orthopantomography is recommendedìto rule out the permanence of the dentitionótemporary or if there is a delay in the eruptionóno final dental, supernumerary teeth and lateral agenesis. Perform radiographic studiesáwe get panoramicámonkeys with orthopantom equipmentógraph to detect possible odontoma.
Frequently the history clíonly familial cleidocranial dysplasia may show:
- clav underdevelopmentíbutt
- om underdevelopmentóplato
- Inability to close the fontanelles
Curiosities of cleidocranial dysplasia
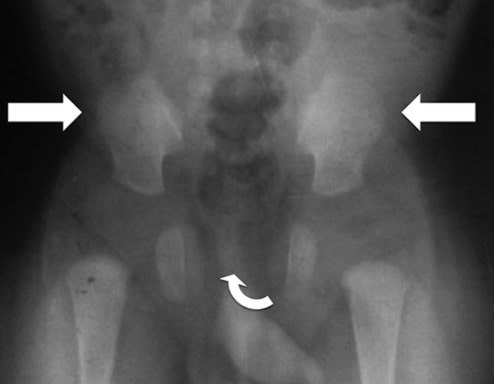 Pregnant women who carry the disease have más chances of having a cesal deliveryárea. onceón is that they have the pelvis más tight than usual, which can impede the passage of the fetal head.
Pregnant women who carry the disease have más chances of having a cesal deliveryárea. onceón is that they have the pelvis más tight than usual, which can impede the passage of the fetal head.
Además, people with this conditionón generally have lower density ósea (osteopenia) and tend to develop osteoporosis. Under this conditionón the bones become progressively más fráagile and brittle at a relatively young age.
In serious case, he does not evenñor may have problems developing age-appropriate motor skills, like crawling or walking.
