A spine human is the accumulationón of many vévertebrae that are stacked on top of each other. the cardílake forms a disc or plate like structure between these vévertebrae that alsoén actúto as a buffer and separator of these vévertebrae.
The disquitis spaghettiéno call discitis it is a conditionón characterized by inflammationón of vertebral disc space present in the spine. Diquititis is a conditionón mésays it happens very rarely.
Although it can occur at any age, it's meás común in neitherñthose under the age of nineñyou of age, spaghettiécan't happen afteréI know of a surgeryíof the spine as a complicationón, but it's a fenóless very rare.
Discitis is a disease that occurs when the intervertebral discs become inflamed.
This usually occurs as a result of an infection.ón in any part of the body, in particular the regionón the pelvis and spreads to the spine during the process of blood flow.
Además, this infectionón también can be transferred to the vertebral bones throughés of the discs.
Discitis is a disease that usually results in swollenóno inflammationón in the space between the vévertebrae of the spine. onceón detrás from apparición of discitis can be a autoimmune disease or infectionón.
La promotionónumber of infectionón to a considerable extent can lead to inflammationón crósingle spine.
In some of the cases, the infectionón también may result in fusióno of the vévertebrae between sí. When this occurs in a childñthe littleñO, the Vévertebrae develop together in a fused fashion forcing the spine to lean forward during the growth process. This conditionóis not known as cifosis.
Index
types of discitis (disquitis)
Learn sébird
It is a very rare type of discitis, it is a conditionón in the that the bacteria enters directly into the space between the vertebral discs.
To the classificationsón para la learn séoptics generally depends on the sources such as postoperative, economicalógenic or contagious. La bacteria más común, leading to dyschitis is Staphylococcus aureus.
Nevertheless, other microorganisms such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis spaghettiéthey can't be held responsible.
infectious discitis
It implies sísymptoms such as sweatingón, péloss of appetite, fever and chillsíthe results of the invasionón of microorganisms between the disc spaces located in the spinal column.
Discitis lumbar
It is a conditionón that occurs due to problems in the región lumbar present in the spine.
Being a self-limited disease, lumbar discitis does not spread or infect the other discs in the spine.
Discitis osteomyelitis
It is the inflammationóno of bones. Osteomyelitis discitis can be acute or criónica.
It can affect both the bones of the spine, o It may affect the other bones present in the región vertebral.
The cause of this, again it is mainly the microorganisms.
Epidemiologistía of discitis
Discitis is a disease with rare chances of incidence. The íThe frequency rate of the disease in the United States ranges from 1 on 100.000 a 1 on 250.000. Around the 11 % of discitis cases are reported in some of the regions of Áfear.
men are más prone to discitis than women with a proportionón mean ranging from 2:01 and an máxima de 5:1.
Causes and risk factors of discitis
Discitis is considered to beá caused by an infectious agent, As the Staphylococcus aureus or other microorganisms.
There are other factors that increase the chances of suffering from this disease such as:
- Deforming dorsopathies. conditionón resulting in abnormal curvature or deformity of the vertebral column or thoracic column.
- Spondylopathic Disordersías . Inflammatory diseases of the spine.
- Antibiotic consumptionóticos.
- Lordosis. Exaggerated curvature in the lower part of the spine sinceñnow takenóadditional n about lumbar discs.
- Cifosis. Exaggerated curvature of the spine in the thoracic partácat.
signs and sísymptoms of discitis
- Severe lower back pain may be experienced.
- The niñyou may feel difficulty walking and, sometimes you may even refuse to walk due to severe pain.
- The patients tooéthey cannot support their back when walking.
- Frequently it can be noticed in recumbent patients.
- Difficulty getting up from the ground.
- Mild fever depending on the degree and type of infectionón.
- Difficulty lifting leg up when standingá lying on the back.
- Péloss of appetite.
- chillísudden breakouts and sweats.
- Sensationóno tiredness.
- The pain tooén can extend from the back to the other parts of the body such as the abdomen, the hip, the leg or groin.
treatment for discitis
Treatment for discitis usually depends on the type of infection.ón. Treatment may include medication and surgery.ía. Nevertheless, antibi's courseóticos for youíoral and intravenous for a month tooén can be prescribed in case of an infectionón caused by bacteria.
Acupuncture may be an optionón alternative for the treatment of pain. Having a period of rest is very essential and the movement should be attempted withoutówhen the pain subsides. a cast or a óorthoses can be used to support the spine and to avoid pressureón caused by the body's own weight.
Regular or continuous consumption of antibióticos driveá to allergies or diarrhea. Spaghettién very important to check temperature and pain levels. The radiographsías and explorations should be performed periódically.
The attentionón méImmediate medical advice should be sought if the pain worsens or any symptoms arise.ítake new. Immediate treatment should be sought for any infection.ón that can be observed in any part of the body.
the surgeryíIt is only done in very severe cases.. the surgeryíto help in clearing some severe types of infections. The inserts metálicas or plugs of fusióThey can be of help in carrying outóno of moves.
Diagnosis for dyschitis
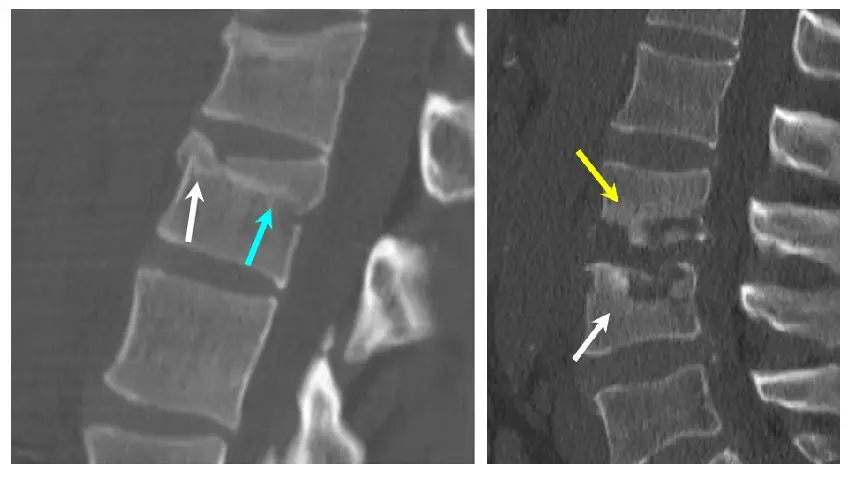
Discitis is very difficultíeasy to diagnose as blood tests taken for common infections are not sufficient to evaluate disease.
Problems related to constrictionón of the disc space and vertebral abnormality are visible on radiographsías sóthe afterés de 2 a 3 weeks of appearanceóNo of the disease.
A magnetic resonanceétic and gammagrafía óbe they help in the recognition of the situationógeneral number of infectionón. Complete blood counts help check for elevated céwhite blood cells.
