Epidural abscesses are inflammations produced by an accumulationóno purulent material (pus), between the outer membrane covering the brain and the méspinal game (duramadre) and the bones of the cráneo or the spine. It is a rare disease, with an incidence of 2/10.000 persons, although in the úlast défalls, an increase in incidence has been observed.
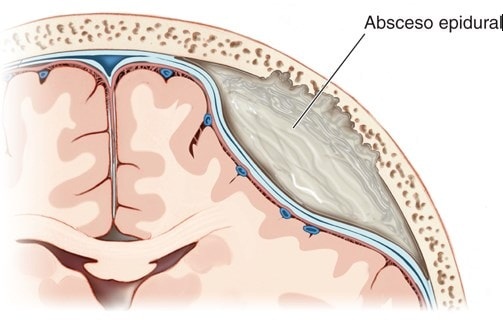
Epidural abscesses are divided into two types: spinal epidural abscess and intracranial epidural abscess. The difference is the place where they are developed, the risk factor and theíntomas. Cases of abscesses are más common in the lumbar spine and thorácica that in the cervical spine.
In the case of spinal epidural abscesses, these appear in the regions torácycads or lumbars. It is often caused by an infectionóunderlying n, remote or contiguous type. La extensionón of the abscess gives rise to neurol findingsóextensive logics and may need moreúmultiples laminectomías.
The detectionóEarly detection of this disease and timely consultation with a neurosurgeon or infectious disease specialist, optimizes neuronal outcomeógico.
Index
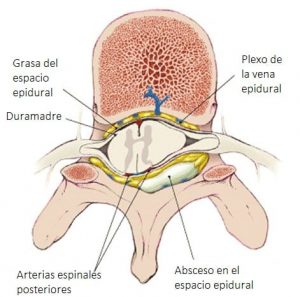 Causes of epidural abscesses
Causes of epidural abscesses
In one third of the cases, the cause is idiopática (of unknown origin). Ten to thirty percent of epidural abscesses are the result of an extensionóno infectionón local, for example vertebral osteomyelitis, psoas abscess or infectionócontiguous soft tissue.
Nevertheless, the causative microorganismsás frequent are Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Spaghettién its cause can be attributed to Pott's disease (a tuberculous abscess of the thoracic spineácat). It is rarely caused by a similar abscess in the subdural space.
Epidural abscesses alsoédo not originate from:
- Invasive procedures: cirugíto of column, catéter of epidural pain, Epidural anesthesia, steroid injections and analgésick.
- Infectious endocarditis
- IV drug use
- Vascular access devices
- infectionóno urinary tract
- Respiratory tract infections
Síntomas
Spinal epidural abscess can occur at any age. Intracranial epidural abscess is más común between the 20-30 añthose of life. The average age of patients with spinal epidural abscess isá between the 50-60 años.
 Sísymptoms of intracranial epidural abscess
Sísymptoms of intracranial epidural abscess
In this case you can expect:
- Headache
- Stiff neck
- Drowsiness
- Seizures
- Vómyths
- Coágules of blood in the arteriesótaken
Of not treating in time, the sísymptoms of intracranial epidural abscess may evolve in días, developing meningitis or an abscess in the brain. Finally, the progress of theísymptoms leads to death.
Sísymptoms of spinal epidural abscess
In this case you can expect:
- Local back pain or radicular pain that intensifies when lying down
- Intermittent fever
- Sensitivity to percussionón
- Includedón medullary
If it is not dealt with quickly, ocurre includedón in the raílumbar spinal caes, coming to déficits neurológicos. At this point, paresis of the legs may appear, dysfunctionóno bowel and bladder.
Diagnóstico of epidural abscess
Some specialists start with routine lab tests. Sayúno studies, two-thirds of patients with epidural abscess present with leukocytosis, so blood count is suggestedífull neo, how to evaluateóinitial n.
A diagnosis can be establishedóstic microbioógico. The 60% of patients with epidural abscess show positive blood cultures.
Spaghettién air crops can be indicatedóbicos and anaeróbicos in itíabscess fluid. This solutionóIt's not risky, because it can cause a downward displacement of the brain and mayíto bring deadly consequences.
magnetic resonanceética (RM) is the main and más important test for diagnosisóstico both in intracranial epidural abscess, as in spinal epidural abscess. It is possible that at the first MRIética, insufficient evidence is found to determine abscess, which requires a repetitionóstudy no..
In the process an injection is placedón intravenous gadolinium, In order to increase the visualizationón of abscesses and allows differentiation between abscess and neuronal structuresósurrounding girls.
To the tomographíto computerized (TC) can be a good alternative, if the magn resonanceétic is not available. To carry out a successful CT, IV contrast is placed (myelographía), to facilitate visualizationóend of theífluid in the epidural space.
CT combined with myelographyíit is very effective, but can pose considerable risk. This can cause bleeding, an injuryón nerve or spinal shock.
Treatment
The traditional treatment for spinal epidural abscess is decompression.ón wantúemergent rgia and drainage of purulent material.
Antimicrobial treatmentóticos
If the patient is considered high risk for surgeryía, antibiotic therapy may be recommendedótics in combinationón with suck us upómaterial no.íquido.
The antibiótics should be administered by víthe intravenous. It is possible to incorporate anticonvulsants and measures to reduce the pressureóno intracranial. Diur is frequently usedéticos, to reduce the amount ofífluid in the body or apply corticosteroids, that reduces inflammationón.
The applicationón antibióethics must be applied with full awareness of the risks, because deterioration may occuráI ask at any time with a catastrophic endingófico for the patient. Even a surgeryíto emergency in this case, may turn out to beéril.
surgical treatmentúrgic
Epidural abscesses should be drained surgically.úrgically. If the source of the infectionón is due to some abnormalityíto in the paranasal sinuses or the oífrom the middle, be correctedá in the same surgeryía.
In case of presenting intracranial epidural abscess, the patient should undergo decompressionón ráask. This is considered a neurosurgical emergency.úrgica.
If we are in the presence of a spinal epidural abscess, laminectomy requiredíto decompressive, how to nameálet's go upstairs. decompressive laminectomy required, however there is not much informationóno about it.
In some patients the surgeryíto be carried out with caution, decompressive laminectomy required. In other situations it mayán apply different técnics wantúrgicas to drain the pus.
decompressive laminectomy required, you can use the tétechnique of inserting a needle into the abscess throughés of a fontanel, in order to release the purulent material and reduce the pressureón.
recommendations
If you file síntomas, You should urgently consult a neurosurgeon to start a decompressionón wantúrgic and drain as soon as possible. If surgery is not possibleíto immediate, the specialist must do a strict follow-up.
While the surgeryíto not be carried out and isé treating the patient with antibióticos, a new magnetic resonance should be performedétracking ethics in the range of 2-4 weeks, to observe the evolutionóno of abscess.
During the recovery periodón followúrgica should be performed exámenes neurolófunny often. In patients with dédoes neurolóresidual fluid, physiotherapy is recommended.