To the radiculologistía is an injuryón that affects the nerves of the spinal column, producing a neuropathyía. It is formed by alterations in the structure óbe and letteríadjacent lakes, as a consequence of somethingúdon't wear the injuryón.
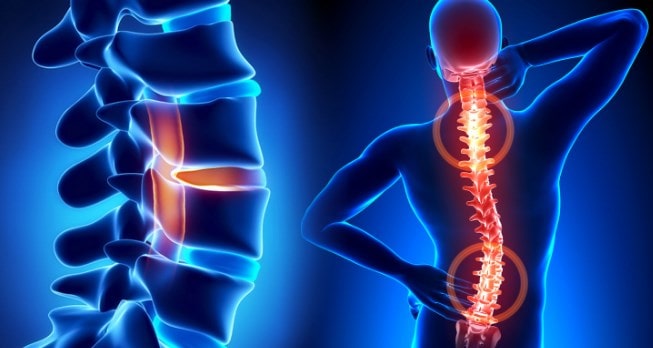
These changes can cause pressureón in a raíz nervous. Frequently causing a pain known as radicular. Spaghettién patients manifest weakness in the extremities, numbness and difficulty controlling certain múdogs.
To the radiculologistícan appear for no reasonón apparent or resulting from spinal cord injuries
To the radiculologistía can occur anywhere on the spine, but the sites más common are in the cervical or lumbar spine. And less frequently in the porción middle of the vertebral column.
If you suffer from pain in your back and suspect a radiculopathyía, hereí we will give you an explanationón detailed description of its main causes, sísymptoms and treatments. Además, we will see the 3 types of radiculopathyíto that they exist and their diagnosisóstico.
Index
Causes of radiculopathyía
To the radiculologistía occurs when a nerve is compressed by surrounding tissue. Sometimes it is caused by a herniated disc spinal.
There are many potential causes, including a tépoor lifting technique, poor posture and back injuries.
This can be caused by a variety of conditions or injuries., including:
 Lift weight
Lift weight- Hernias and tumors
- Osteoarthritis or spinal arthritis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Scoliosis
- Spinal stenosis
- compression fracturesón
- spurs óbone and degenerative disc disease
- Diabetes
- Ciática
- Family history and being overweight
- Aging and poor posture
- Repetitive movements
Síntomas
The sísymptoms of radiculopathyícan range from mild to severe. This according to the nerves that are affected. It manifests mainly with pain, numbness and sensationóNo punctures to arms or legs.
It's likeún that the patients alsoén have localized neck or back pain. Some have increased sensitivity, feeling pain to the touch áaffected area.
 Other common signs of this conditionón sound:
Other common signs of this conditionón sound:
- Sharp pain that begins in the back and spreads to the foot
- Numbness or weakness in the leg and foot
- Sensationóno reflex changes, hypersensitivity
- Increased pain with movement of the neck or head.
- Sharp pain when sitting or coughing
- Numbness or tingling in the back or leg
- Arm or shoulder pain
types of radiculopathyía
They can be classified 3 types of radiculopathyíaccording to your positionón inside the spine, these are: cervical, lumbar y torácat. thenón, we will see the charactersím sticsás important of each of them.
1.- Radiculopathyía cervical
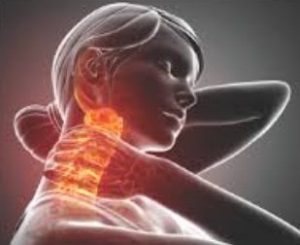
To the radiculologistíto cervical is when the raíz nerve of the spine is affected in the neck area. Generally causing takenónot about her. Can cause lassitude, ardor, péloss of feeling in the shoulders, brazos, hands or fingers.
2.- Radiculopathyía lumbar
To the radiculologistíThe lumbar pain occurs in the lower part of the back and the hip, generating pain in that area, radiates from the back of the thigh to the leg.
It is caused by the dayñor in one of the lower segments of the vertebral column, going from L1 to S1 caused by compressionóno of the raínerve stems coming out of the spinal column.
3.- Radiculopathyía torácat
To the radiculologistía toráCica is a hobbyónot infrequent that can be misdiagnosedójust like complications of the heartón, the abdomen or you see itígallbladder.
A person may experience pain in the chest and torso when a compression occurs.óno or irritationón nervous in the regionómid back.
Diagnóstico
To diagnose radiculopathyía, are méI say first performá an exam níphysical. Later, may perform certain tests or scans. Además of the examísico and I reviewed itón of the síntomas, the Médoctors can diagnose radiculopathyíthrough:
 Imágenes radiolóx-ray pictures
Imágenes radiolóx-ray pictures- magn resonanceética
- Scanneríthe computerized ones
- impulse testéelectrical called electromyographyía o EMG.
- Electromyogram to measure impulsesécitrus of the múdogs
- driving studyón nerve to measure the ability of the nerves to send signalsñales theéctrics
Treatment
To the radiculologistía is treatable without surgeryía. Depending on the severity of the conditionón and other health conditions, the MéDoctors may recommend certain medications, within which isán: analésick, anti-inflammatory, applyóno ice and heat.
the use of necklaceín cervical, therapy fíPhysical exercise and rest at home can help relieve symptoms.íntomas.
When treatments do not quirúrgic cease to be effective, the Médoctors recommend performing surgeryíto treat oppressionón generated in the nerve.
Some surgical proceduresúrgic include repairón of a disc herniation, the enlargementón of the space of the spinal canal, take it outón of a spurón ówhere are their tiesóno of bones.
It is recommended to take care at home and use combination treatments.