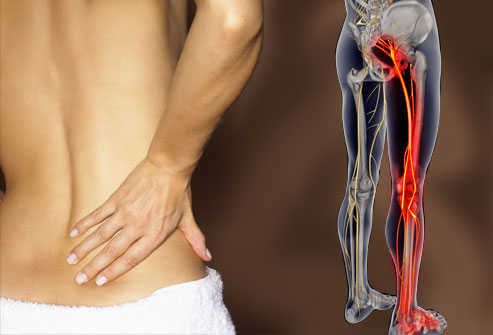
This pathology is one that causes a pain that extends from leg to foot, that means that it is very common for people to confuse it with the lumbago, But it is not the same; it is not necessary that in all occasions the pain reaches the foot, it can stay many times in part of the extremity nothing more.
Another thing that can include this annoying pain is that there is a lack of sensation in the extremity or a lack of strength as well., it can occur at any time both day and night and you can recognize it much more specifically if when you get into the fetal position you feel that it is totally or partially relieved.
The main difference between this pain and the pain of lumbago or sciatica, is that the previous ones are strictly limited to the lower back or the buttocks as well, while this pain runs from the buttock to the foot, along the way it passes through the back of the thigh and calf.
Index
What causes lumbosciatica
The main reason why course pain is generated and wins most of the time is that there is a hernia nucleus culposus in some part of the lumbar canal occupying space, specifically near the roots of the sciatic nerve and compress it, why the pain is so sharp and spreads so wide.
We've talked before about the spinal discs in our spine simply aging by nature., but something that we may not have mentioned is that not everyone ages at the same rate; when one of the discs gets older this automatically causes it to lose liquid and the more you decide to try, more ruptures occur that make the disc smaller and all this is what causes a herniated nucleus to occur at some point.
How lumbosciatica is diagnosed
To give a clinical diagnosis to the patient and to know if he suffers from bearings and his reflexes have to be evaluated, his sensitivity and his strength, usually this by means of the joints or a general physical exam; depending on the levels of reflex strength and sensitivity of the patient, whether tall or short, the doctor can know specifically at what level of your spine you can give the hernia.
If as a result of this examination the doctor suspects lumbosciatic, then ask the patient for a simple x-ray of the lumbar spine and if it gives an overview that this is the problem, the diagnosis will be completed with a magnetic resonance imaging, the one that will help show exactly how the disks are, the hernia and which of all the roots is involved.
Treatment of lumbosciatica
The 80% of people with this problem can reduce it with painkillers, medications that are targeted at neuropathic pain and with anti-inflammatories, local heat can also be used, physiotherapy or rehabilitation; when this doesn't fix it there probably needs to be surgery.