A laminectomy or decompressive laminectomy is a surgical procedure that seeks to remove the bony arch of the vertebra that covers the nerve, known as lamina. This technique relieves pressure on the spinal nerves and the spinal cord.. It is frequently used in the treatment of spinal stenosis and the vertebral arthrodesis.
When non-invasive treatments fail, a laminectomy is necessary to relieve symptoms that interfere with daily life. Candidates for a laminectomy have:
- Constant back pain of severe magnitude.
- Dificulty to walk.
- Weakness or numbness in the legs.
- Incontinence.
These symptoms are typical of a narrowing of the spinal canal that puts pressure on the spinal cord. If this narrowing is located in the upper part of the spine (narrow cervical canal), a cervical laminectomy should be performed. If it is located in the lower back (narrow lumbar canal) lumbar laminectomy recommended.
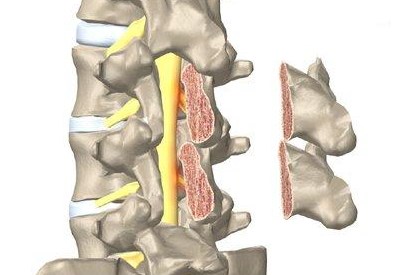
Narrowing of the spinal canal causes disorders including degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, herniated disc, osteophytosis or espondylosis. In many cases, two or more of these conditions can occur together..
Index
Laminectomía Cervical
It is a surgical intervention that is performed at the neck level, on its back. A scheduled removal of spinal canal laminae or any other soft tissue that may be causing compression on the spinal cord is performed.
The reasons for undergoing a cervical laminectomy are varied, but mainly to treat pressures on spinal nerves in the neck and also as a method to stabilize the cervical spine.
What happens in the back neck?
The spinal canal is a bony tunnel in the spine, in which the cord and spinal nerves are located. When this tunnel is reduced in size, the spinal nerves and / or the spinal cord are compressed, putting pressure on them.
At this time the symptoms of pain appear, numbness, Tingling sensation, general stiffness and weakness. When it is at the cervical level, it usually manifests itself in the shoulders, arms and hands.
Lumbar Laminectomy
Lumbar laminectomy is also known as open lumbar decompression and is applied for degenerative disorders. Commonly performed to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
It is a technique designed to remove part of the bone above or below the nerve root in order to free space. The procedure involves an incision of 5 a 12 cm in the midline of the back and approaching the spine laminectomy is applied to reach the nerve roots.
It is the last resort used when non-invasive measures have already failed: injections, medicines, physiotherapy, etc.
What happens in the lower back?
The intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers and allow movement of the bones of the spine in the lower back.. When those discs shrink, cause pain, numbness and weakness in the legs. This can lead to herniated disc which in most cases is treated with a laminectomy.
Laminectomy preoperative
- If you are a smoker, it is a good time to quit.
- Stop any drug that makes it difficult for the blood to clot, such as acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, naproxen, among others. Consult the doctor which medications can be ingested in the period prior to surgery.
- Tell the treating doctor if you suffer from any disease or health problems.
- The day of the surgery it is recommended to go without drinking or consuming food, at least 8 hours before the intervention.
Postoperative laminectomy
After surgery, the medical staff will most likely invite you to get up and walk., to check that motor functions were not impaired. Most people who have laminectomy leave the hospital in 1 a 3 days, if no complications arise.
Follow the surgeon's instructions to take care of your back at home and you will be back to your work routine in no time..
5 Benefits of a laminectomy
The goal of a laminectomy is to eliminate the symptoms of a narrowing of the spinal canal., like pain, numbness, tingling and weakness. In other words, restore all nerve function.
After a laminectomy the following benefits should be achieved:
- Total or partial pain relief.
- Decompression on the spinal cord and nerves. Strength does not completely return to normal, but the weakness improves remarkably.
- Prevention of deterioration and abnormal movement of the spine.
- Considerable reduction in drug administration.
- General stabilization of the spine and prevention of further damage.
Risks of a laminectomy
- Infection. In the wound and / or the bones of the spine.
- Constant pain that doesn't go away.
- Loss of sensation due to spinal nerve damage (with probabilities of occurrence less than 1%).
- Sexual impotence.
- Incontinence.
Even so, if a laminectomy is not performed on time, it may make the disease worse and begin to have trouble walking, maintaining balance and a gradual deterioration of motor functions that can lead to paralysis.