The vertebral column or spine begins at the coccyx and ends at the skull, forming a single unit, a single vertical organ. This implies that when we feel any discomfort, pain or problem in any part of the spine, it is mandatory to review the whole set in general.
Index
Functions of the spine
It is the main support of the human body and the skull, helps support the total weight of the body and protect the spinal cord. The bones that make up the spine are the vertebrae that make the spine an articulated joint..
The spine allows the human being an upright position and vertical movement (standing).
• Keeps the trunk upright thanks to the muscles and ligaments and stabilizes the trunk resisting the force of gravity.
• Another function of the spine is the articulation of the body., thanks to the vertebrae that make up the spine and that are linked together as if they were gears.
• The muscles, the diaphragm and intestines among other organs, are anchored to the spine.
• Protects the spinal cord, which is a very fragile nervous tissue that can be damaged by sudden effort or movement.
Spinal cord
The spinal cord it is very important as it is an extension of the brain, hence it is protected between the vertebrae of the spine.
Measures about 45 centimeters long and is protected by layers called meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. Its extension is from the brain, hasta la primera vértebra lumbar y desde ahí se “abre” formada la comúnmente denominada “cola de caballo”.
It is made up of millions of nerves, who are in charge of sending information through the body and from the brain.
Column structure
The spine is made up of vertebrae and between each of them there is a disc, which is called the intervertebral disc, allowing the spine mobility and flexibility. The vertebrae are called differently, depending on the area they occupy in the column: cervical, thoracic and lumbar.
If we look at the column from the side, two types of natural curves are perceived which are called lordosis and kyphosis. The form of kyphosis in the skeleton has the function of protecting an organ, while the curvature in the form of lordosis, the spine commonly uses it for movement.
Thanks to the low or lumbar spine, movements of the lower extremities (the legs) and the superiors (the arms), they are totally independent.
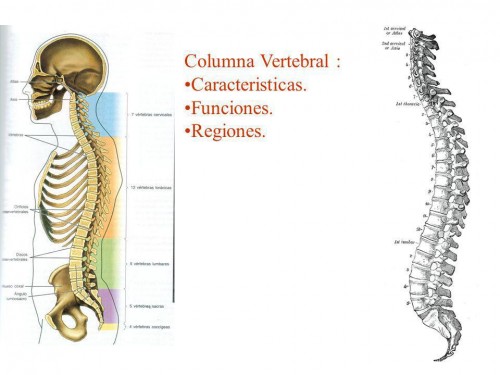
Different vertebral areas
As in the different curves presented above, if we view the column from the side, we can distinguish three well differentiated areas of the spine:
• Cervical Region. It is located in the upper area, with concave curvature in the shape of lordosis, also called cervical lordosis and with 7 vertebrae named C-1 through C-7.
• Dorsal region. It is the middle area of the back and its convex curvature is of kyphosis or dorsal kyphosis. Make it up 12 vertebrae named D-1 through D-12. Some specialists call them T-1 to T-12.
• Lumbar region. Lower back and concave curve shape is lordosis or lumbar lordosis. Is composed of 5 vertebrae named from L-1 to L-5.
These areas are made up of mobile vertebrae and are a total of 24.
There are two more areas in the lower area of the spine, whose vertebrae are welded and therefore immobile:
• Sacred Zone. Contains 5 vertebrae named S-1 to S-5.
• Coccygeal area. Contains 4 vertebrae named from Cx-1 to Cx-5.